Monkey - online puzzles
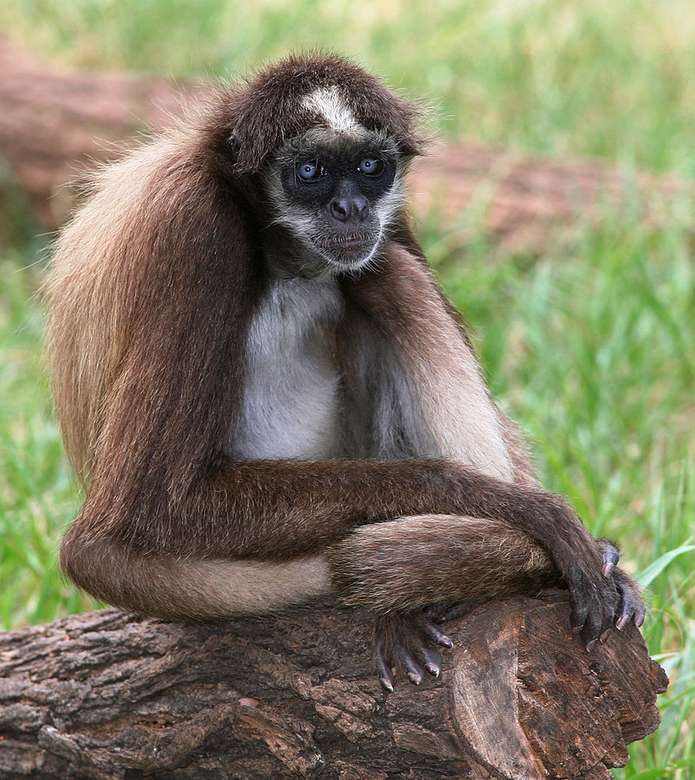
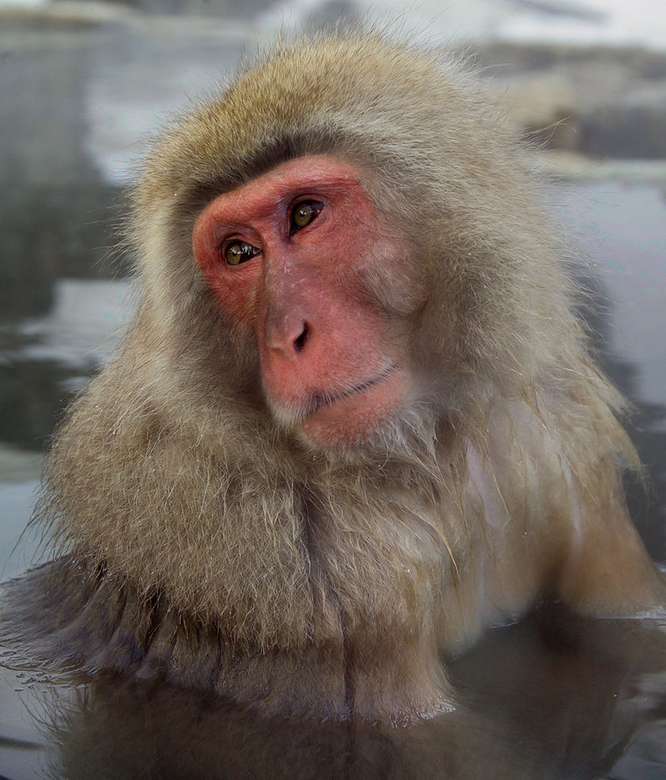





















































Online puzzle Monkey
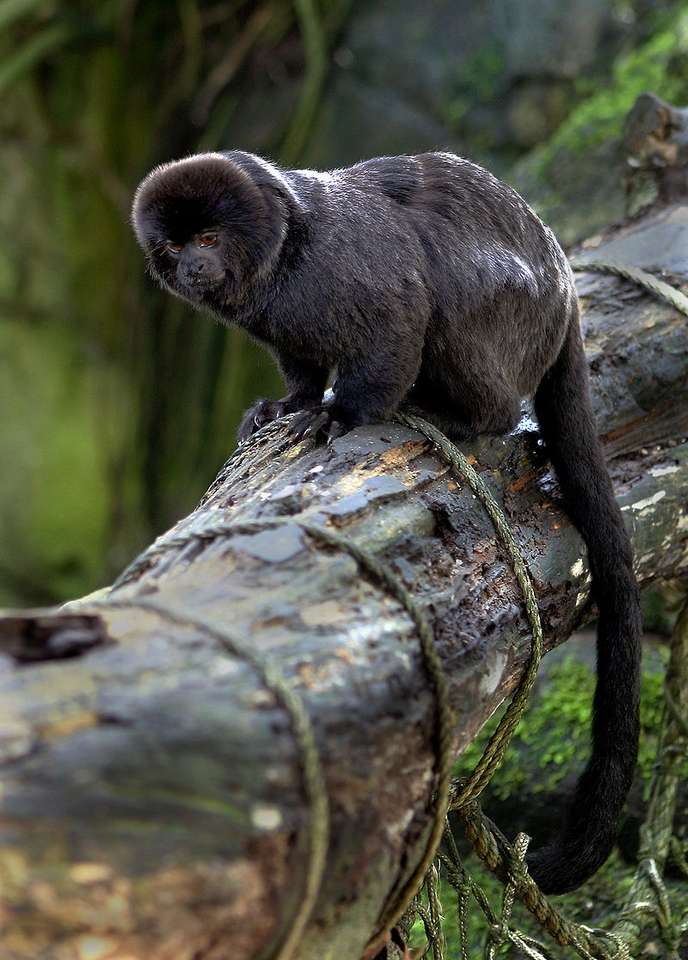
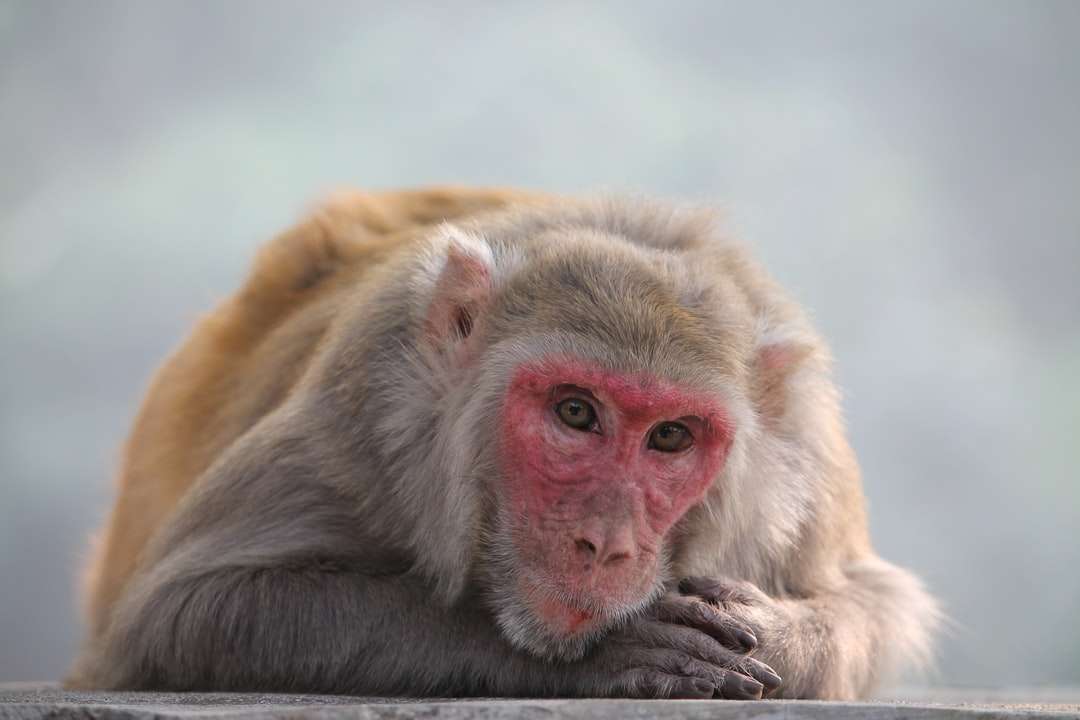
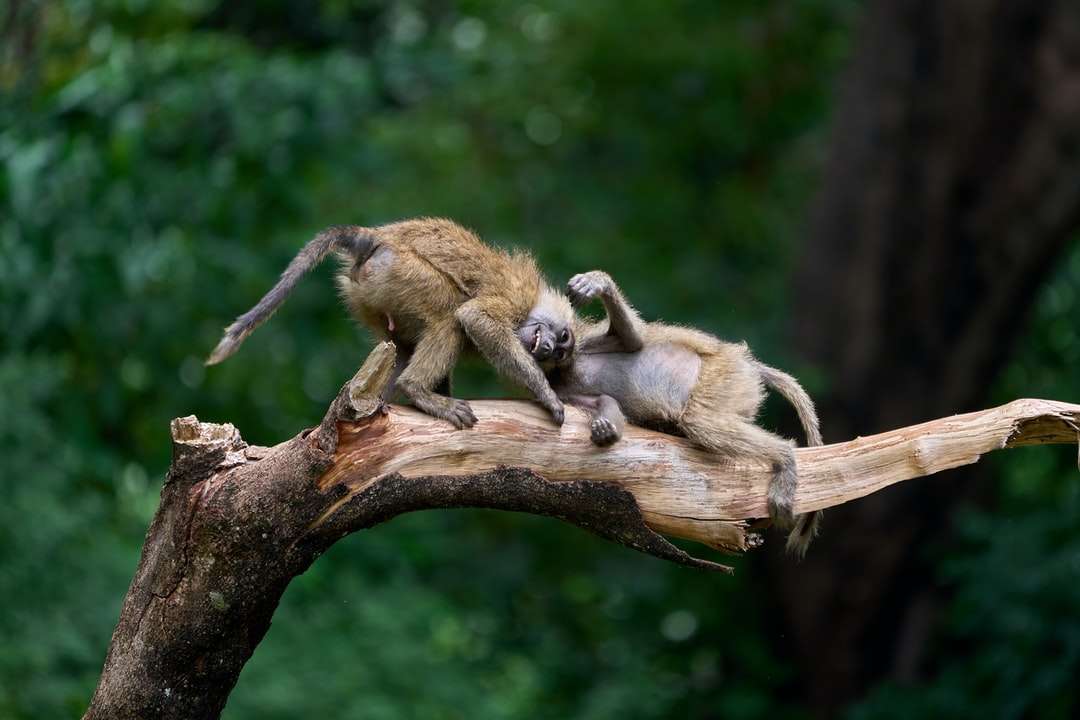
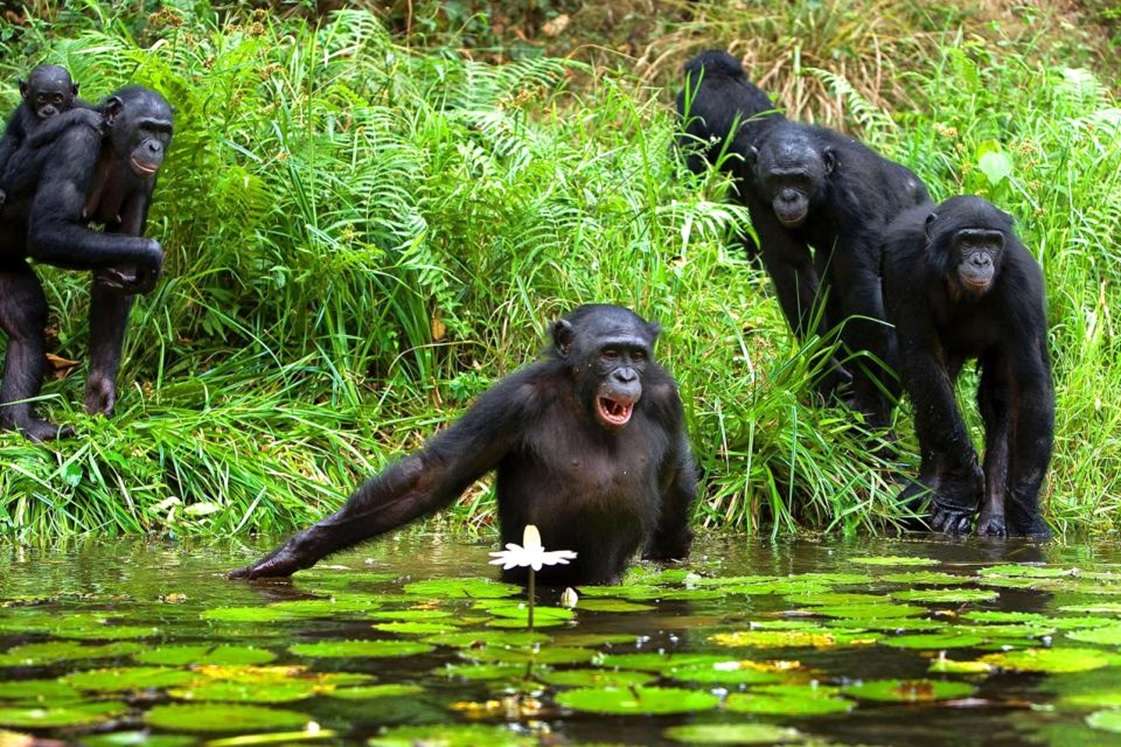
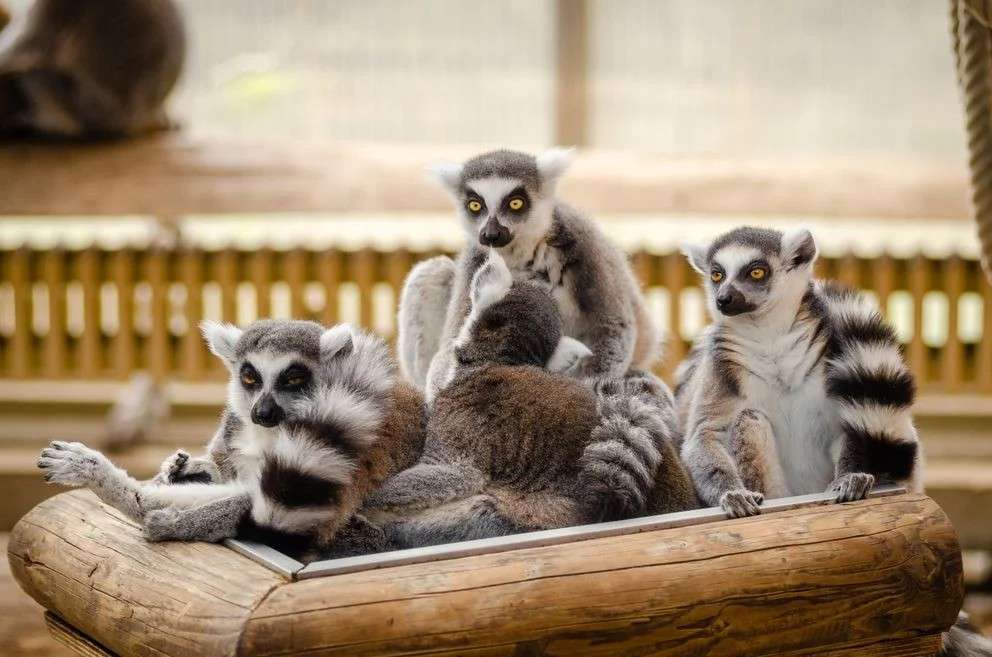
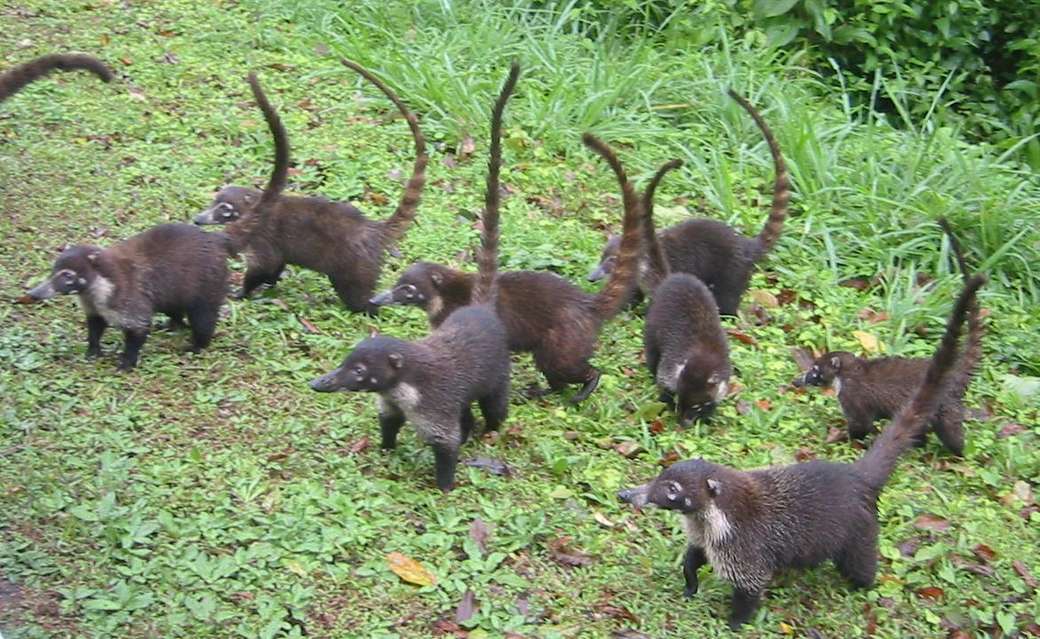
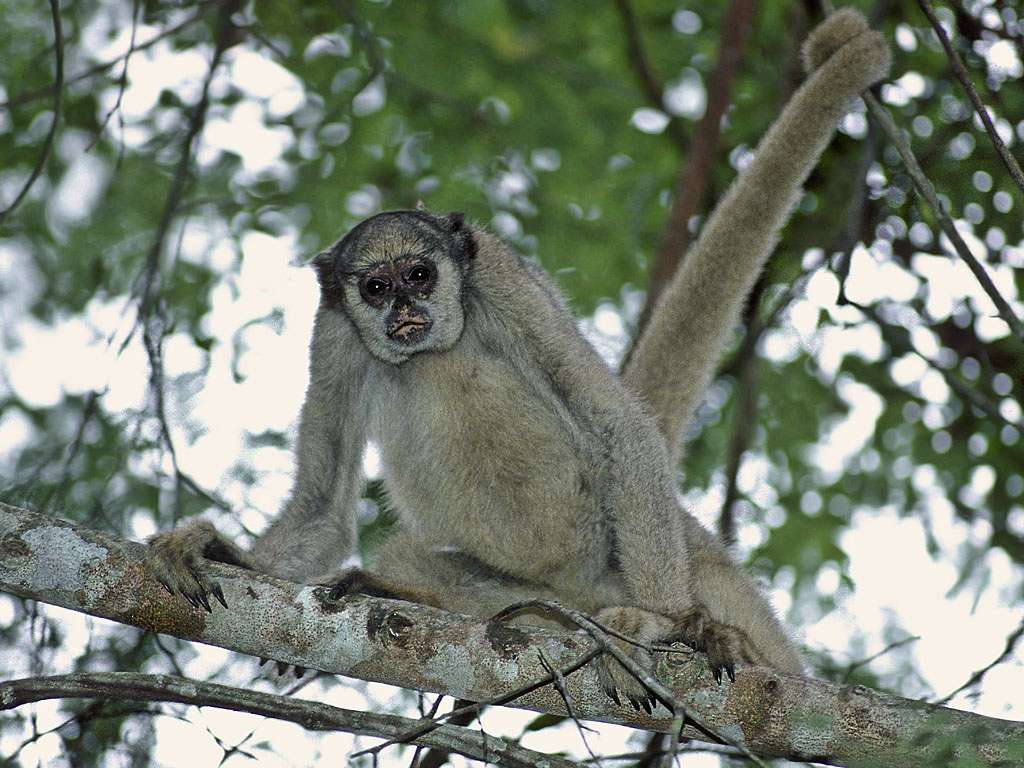
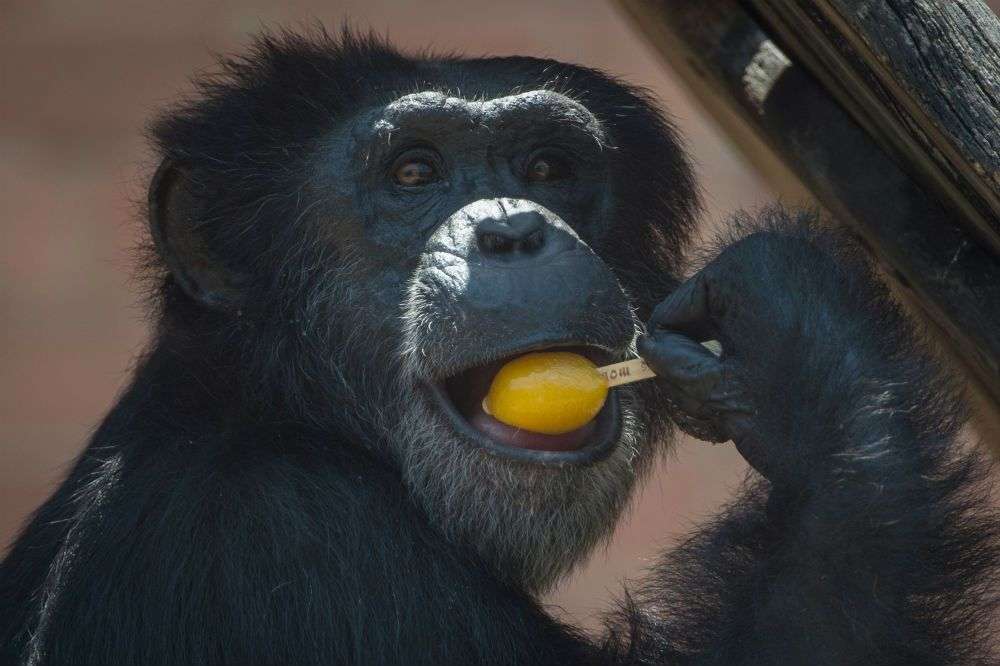
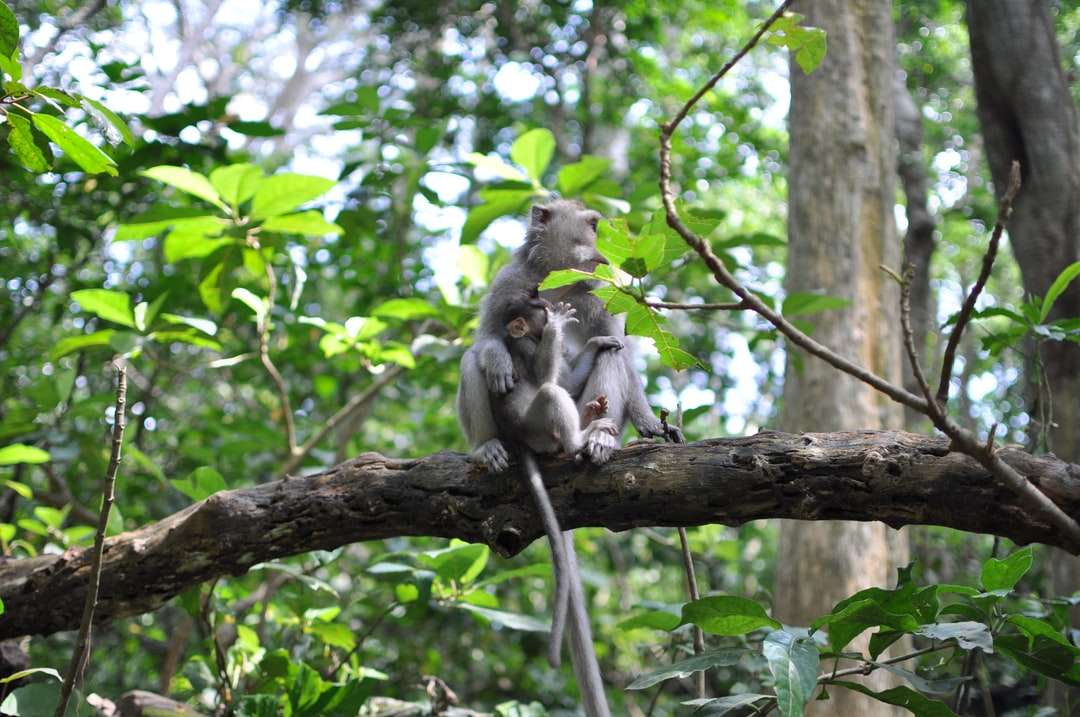
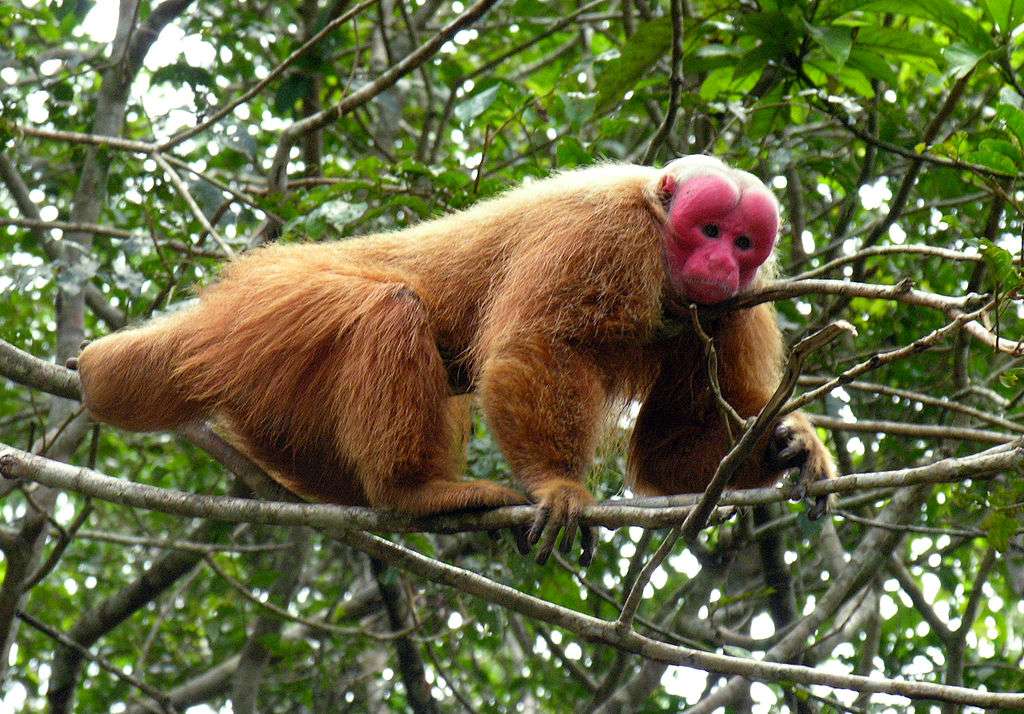
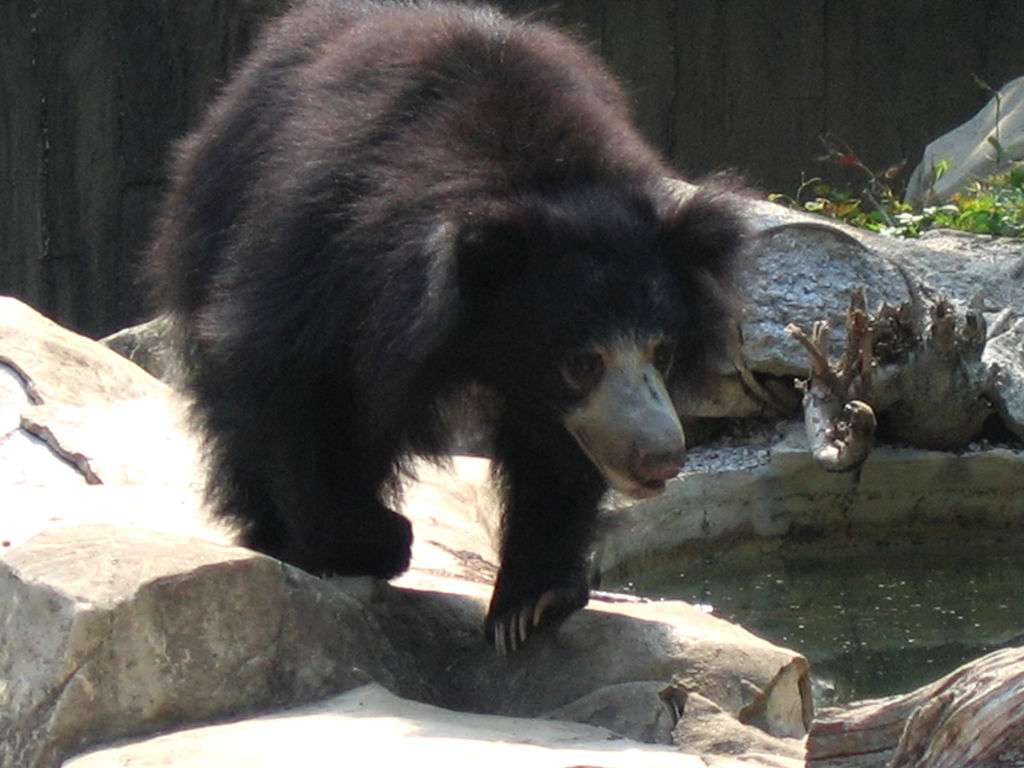
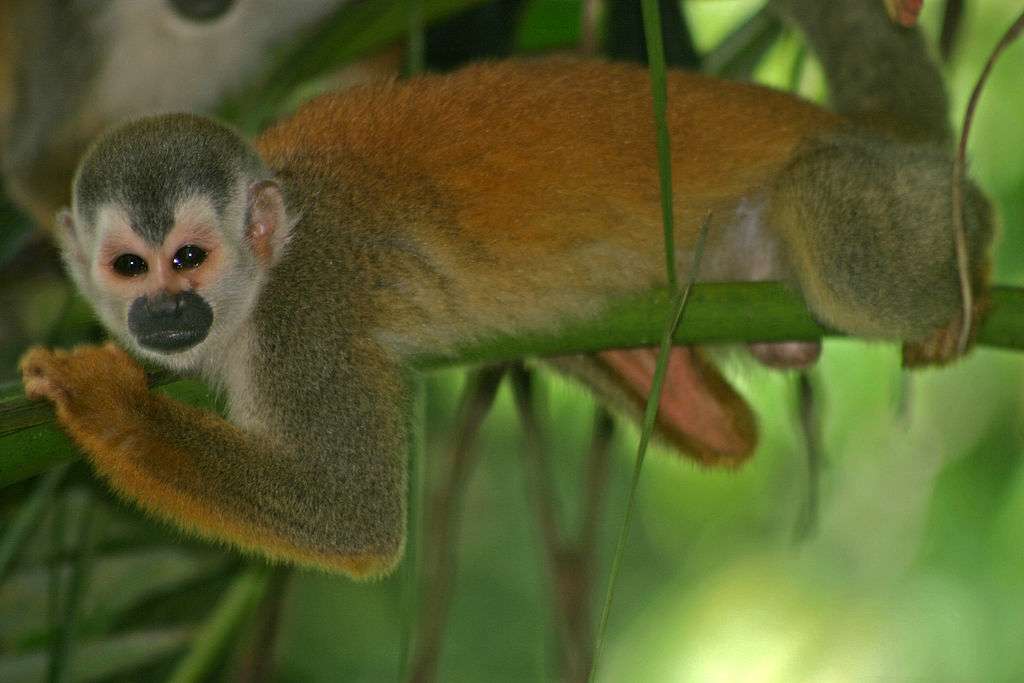
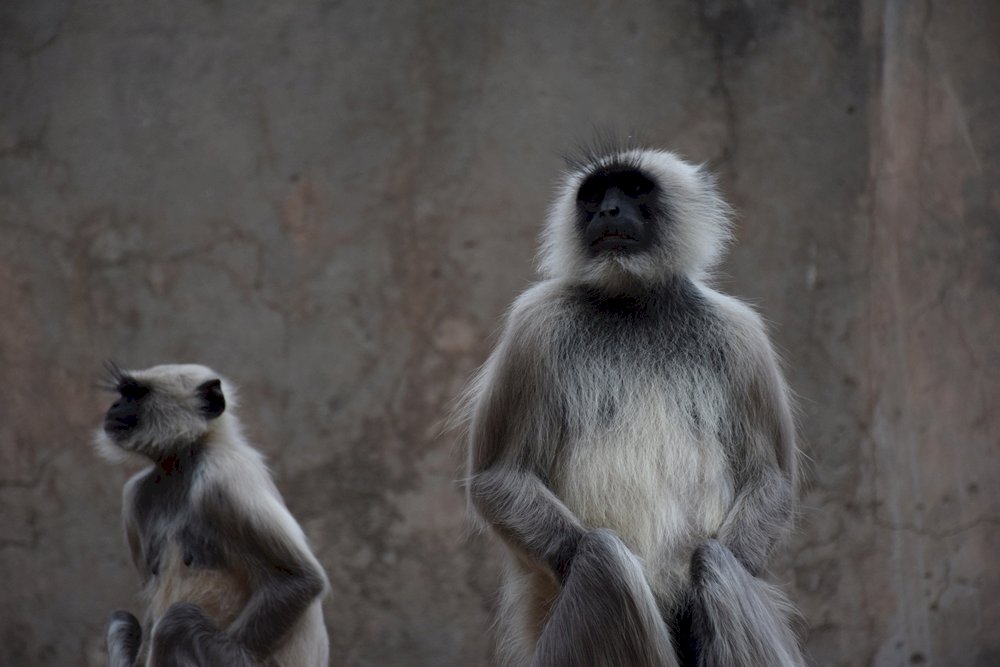
Monkeys are non-hominoid simians, generally possessing tails and consisting of about 260 known living species. Many monkey species are tree - dwelling (arboreal), although there are species that live primarily on the ground, such as baboons. Most species are also active during the day (diurnal). Monkeys are generally considered to be intelligent, particularly Old World monkeys.
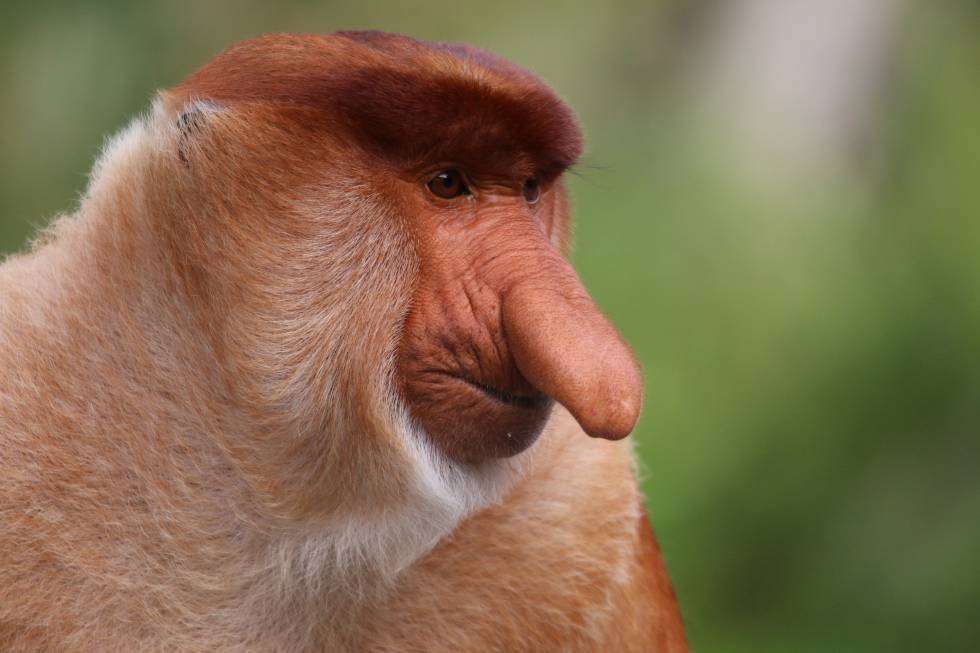
There are two major types of monkey: New World monkeys (platyrrhines) from South and Central America and Old World monkeys (catarrhines of the superfamily Cercopithecoidea) from Africa and Asia. Apes (hominoids)—consisting of gibbons, orangutans, gorillas, chimpanzees, and humans—are also catarrines but are classically distinguished from monkeys. (Tailless monkeys may be called "apes", incorrectly according to modern usage; thus the tailless Barbary macaque is sometimes called the "Barbary ape".) Simians and tarsiers emerged within haplorrhines some 60 million years ago. New World monkeys and catarrhine monkeys emerged within the simians some 35 million years ago. Old World monkeys and Hominoidea emerged within the catarrhine monkeys some 25 million years ago. Extinct basal simians such as Aegyptopithecus or Parapithecus [35-32 million years ago] are also considered monkeys by primatologists.
