Suidae - online puzzles
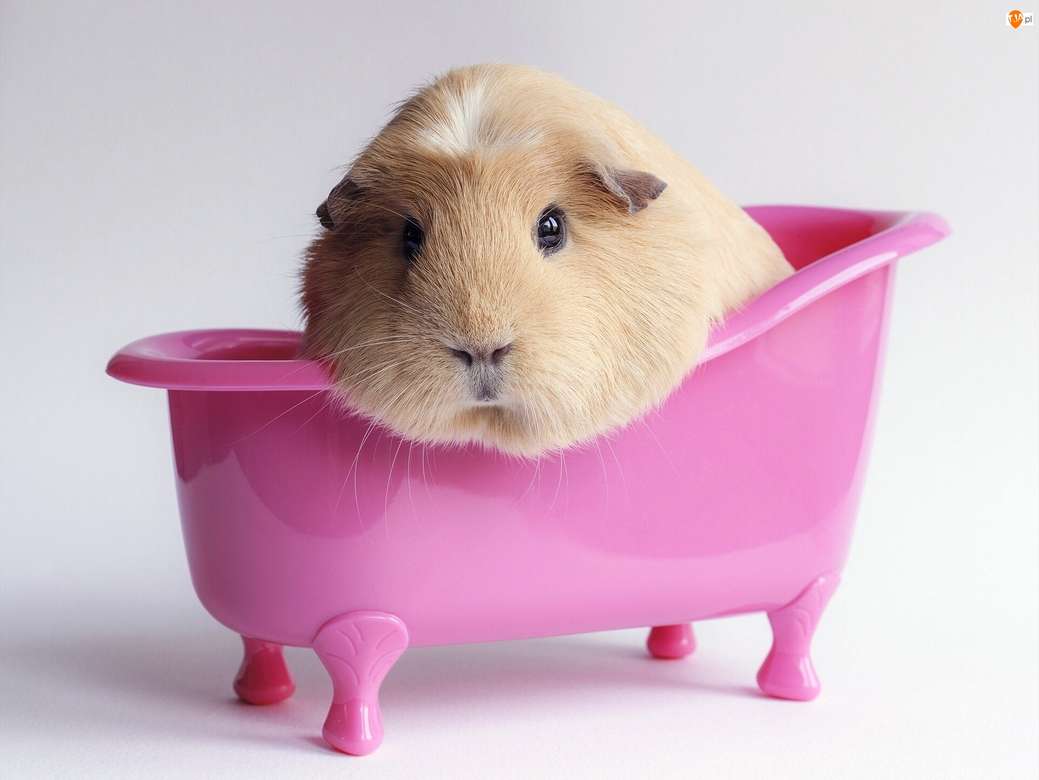
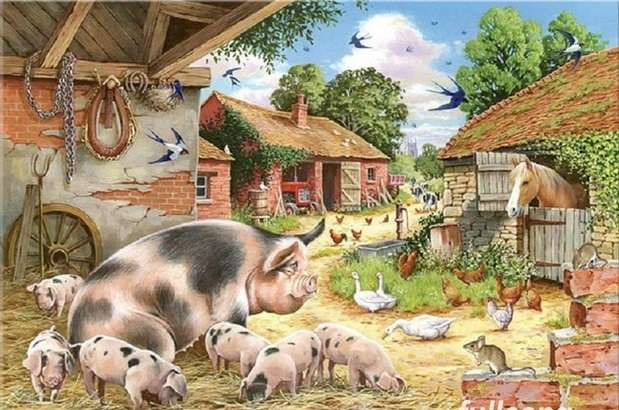
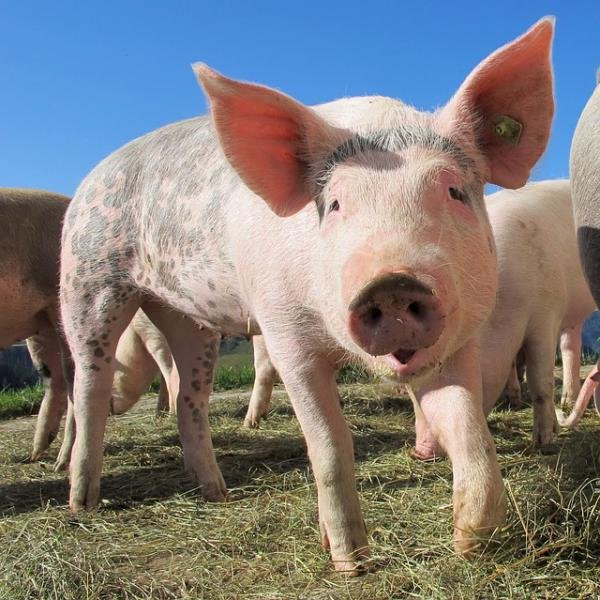






















































Online puzzle Suidae
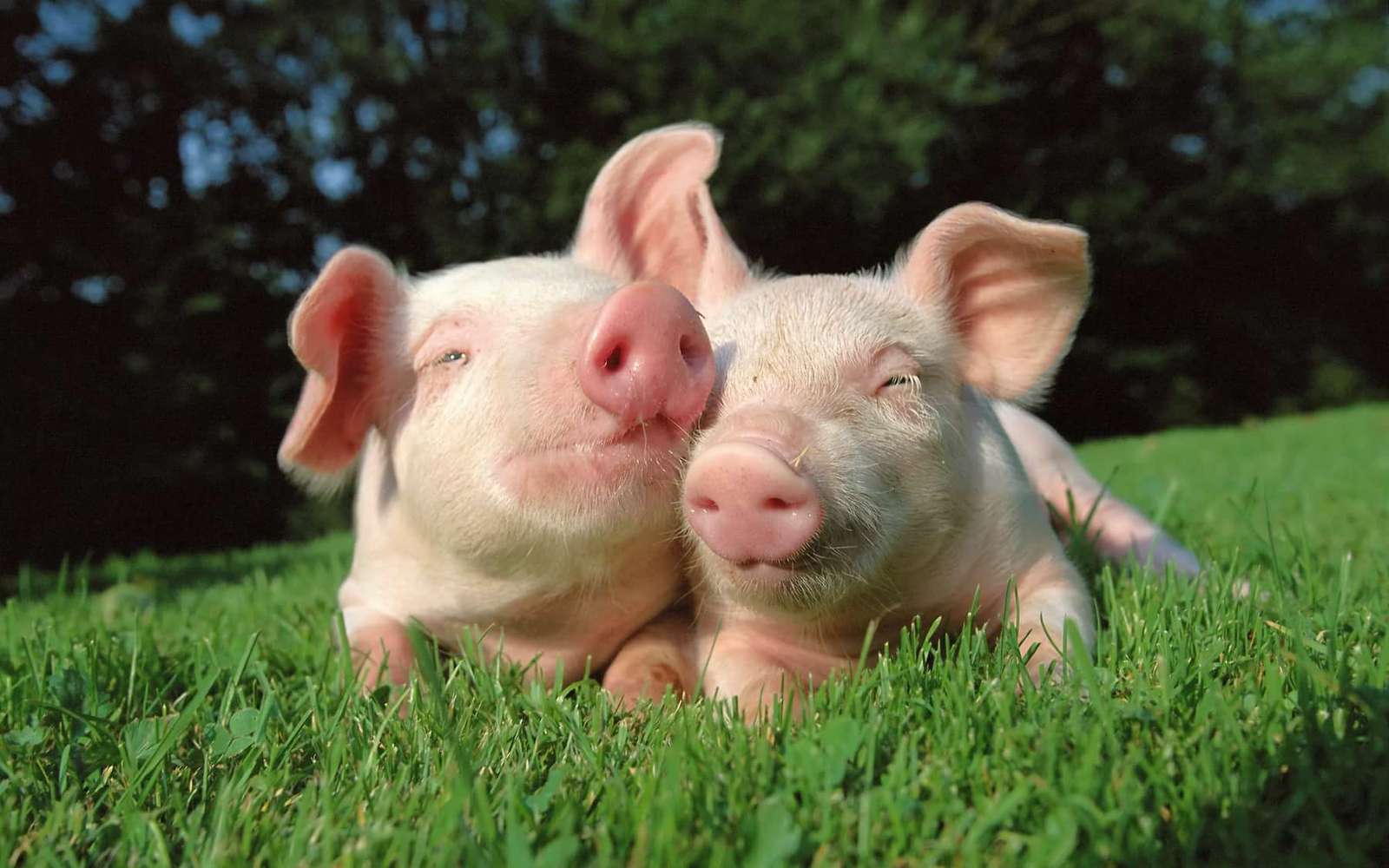
Suidae is a family of artiodactyl mammals which are commonly called pigs, hogs or boars. In addition to numerous fossil species, 17 extant species are currently recognized (or 18 counting domestic pigs and wild boars separately), classified into between four and eight genera. The family includes the domestic pig, Sus scrofa domesticus or Sus domesticus, in addition to numerous species of wild pig, such as babirusas and warthogs. All suids, or swine, are native to the Old World, ranging from Asia to Europe and Africa.
The earliest fossil suids date from the Oligocene epoch in Asia, and their descendants reached Europe during the Miocene. Several fossil species are known and show adaptations to a wide range of different diets, from strict herbivory to possible carrion- eating (in Tetraconodontinae).
Physical characteristics
Suids belong to the order Artiodactyla, and are generally regarded as the living members of that order most similar to the ancestral form. Unlike most other members of the order, they have four toes on each foot, although they walk only on the middle two digits, with the others staying clear of the ground. They also have a simple stomach, rather than the more complex, ruminant, stomach found in most other artiodactyl families.They are small to medium animals, varying in size from 58 to 66 cm (23 to 26 in) in length, and 6 to 9 kg (13 to 20 lb) in weight in the case of the pygmy hog, to 130–210 cm (4.3–6.9 ft) and 100–275 kg (220–606 lb) in the giant forest hog. They have large heads and short necks, with relatively small eyes and prominent ears.