Drupe - online puzzles
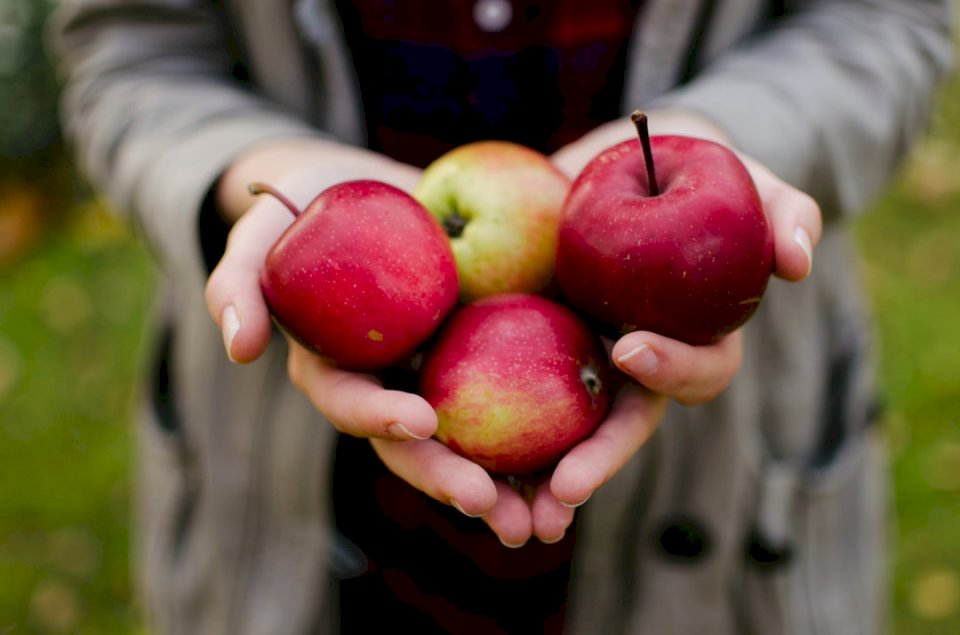

























Online puzzle Drupe
In botany, a drupe ( or stone fruit ) is an indehiscent fruit in which an outer fleshy part (exocarp, or skin ; and mesocarp, or flesh ) surrounds a single shell (the pit, stone, or pyrene) of hardened endocarp with a seed (kernel) inside. These fruits usually develop from a single carpel, and mostly from flowers with superior ovaries (polypyrenous drupes are exceptions).
The definitive characteristic of a drupe is that the hard, "lignified" stone ( or pit, as in a peach ) is derived from the ovary wall of the flower. In an aggregate fruit, which is composed of small, individual drupes ( such as a raspberry ), each individual is termed a drupelet, and may together form an aggregate fruit, although not classifying botanically as a berry. Other fleshy fruits may have a stony enclosure that comes from the seed coat surrounding the seed, but such fruits are not drupes.
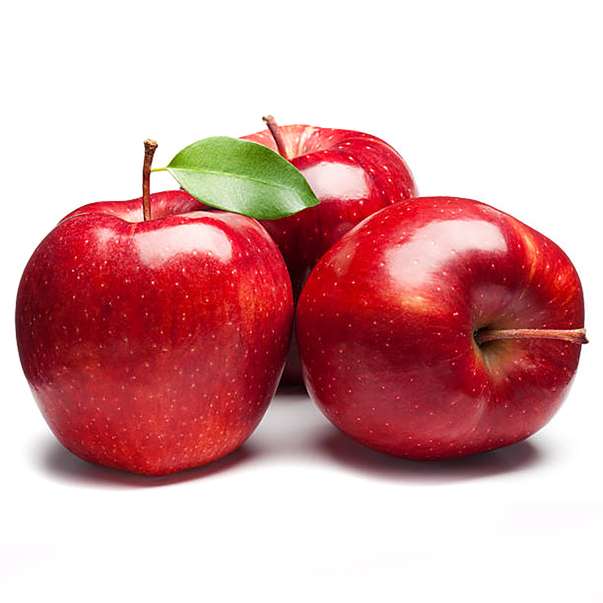
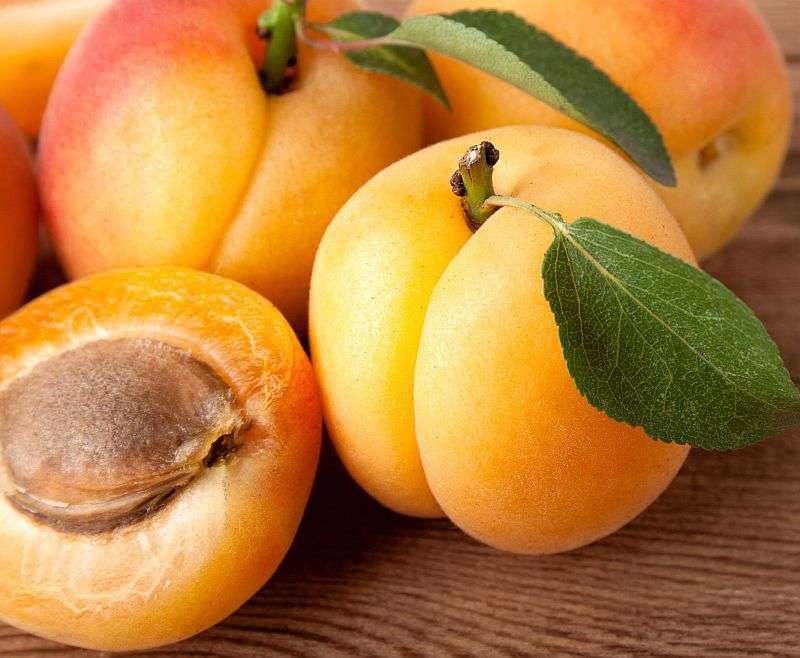
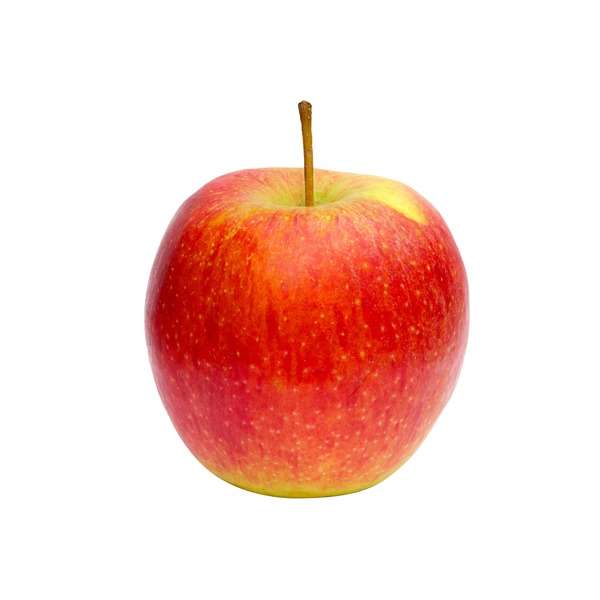
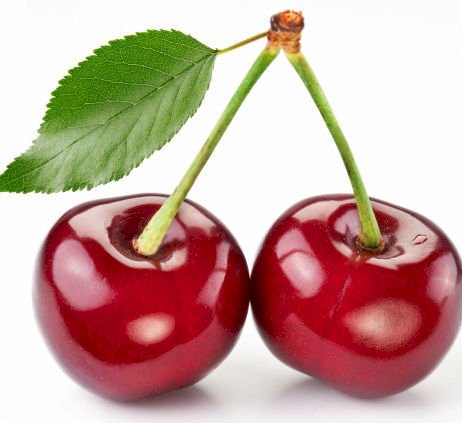
Some flowering plants that produce drupes are coffee, jujube, mango, olive, most palms (including açaí, date, sabal, coconut and oil palms), pistachio, white sapote, cashew, and all members of the genus Prunus, including the almond, apricot, cherry, damson, nectarine, and plum.
The term drupaceous is applied to a fruit having the structure and texture of a drupe, but which does not precisely fit the definition of a drupe.
Terminology
The boundary between a drupe and a berry is not always clear. Thus, some sources describe the fruit of species of the genus Persea, which includes the avocado, as a drupe, others describe avocado fruit as a berry. One definition of berry requires the endocarp to be less than 2 mm (3⁄32 in) thick, other fruits with a stony endocarp being drupes.