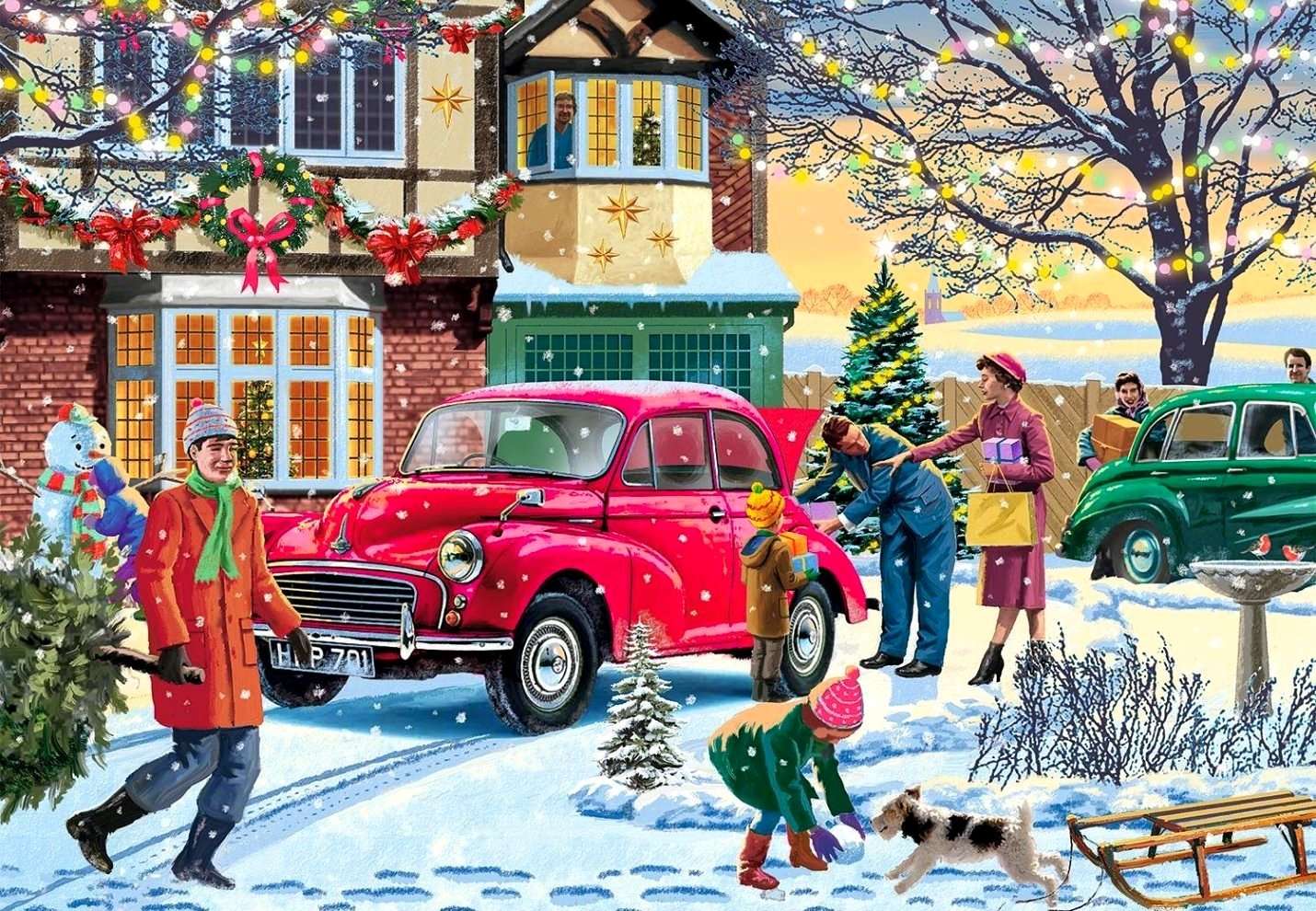
Precipitation - online puzzles




















































Online puzzle Precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravity. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, graupel and hail. Precipitation occurs when a portion of the atmosphere becomes saturated with water vapor, so that the water condenses and "precipitates". Thus, fog and mist are not precipitation but suspensions, because the water vapor does not condense sufficiently to precipitate. Two processes, possibly acting together, can lead to air becoming saturated: cooling the air or adding water vapor to the air. Precipitation forms as smaller droplets coalesce via collision with other rain drops or ice crystals within a cloud. Short, intense periods of rain in scattered locations are called "showers."
Moisture that is lifted or otherwise forced to rise over a layer of sub- freezing air at the surface may be condensed into clouds and rain. This process is typically active when freezing rain occurs. A stationary front is often present near the area of freezing rain and serves as the foci for forcing and rising air. Provided necessary and sufficient atmospheric moisture content, the moisture within the rising air will condense into clouds, namely stratus and cumulonimbus.
