Pleasure - online puzzles



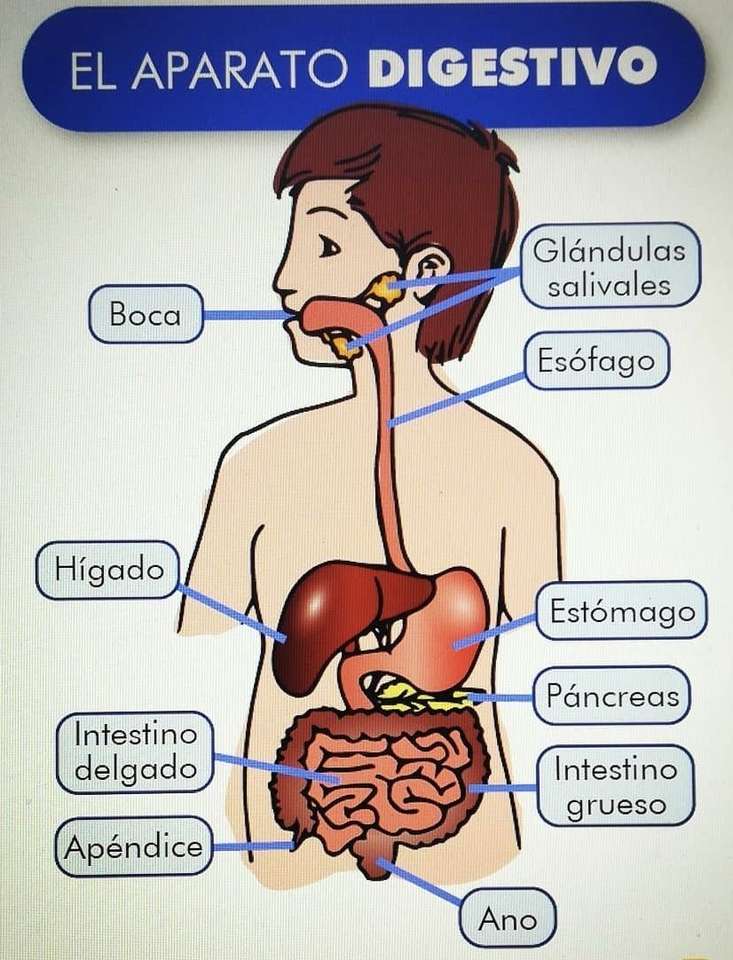














































Online puzzle Pleasure
Pleasure
Pleasure is experience that feels good, that involves the enjoyment of something. It contrasts with pain or suffering, which are forms of feeling bad. It is closely related to value, desire and action: humans and other conscious animals find pleasure enjoyable, positive or worthy of seeking. A great variety of activities may be experienced as pleasurable, like eating, having sex, listening to music or playing games. Pleasure is part of various other mental states such as ecstasy, euphoria and flow. Happiness and well-being are closely related to pleasure but not identical with it. There is no general agreement as to whether pleasure should be understood as a sensation, a quality of experiences, an attitude to experiences or otherwise. Pleasure plays a central role in the family of philosophical theories known as hedonism.