Cetacea - online puzzles
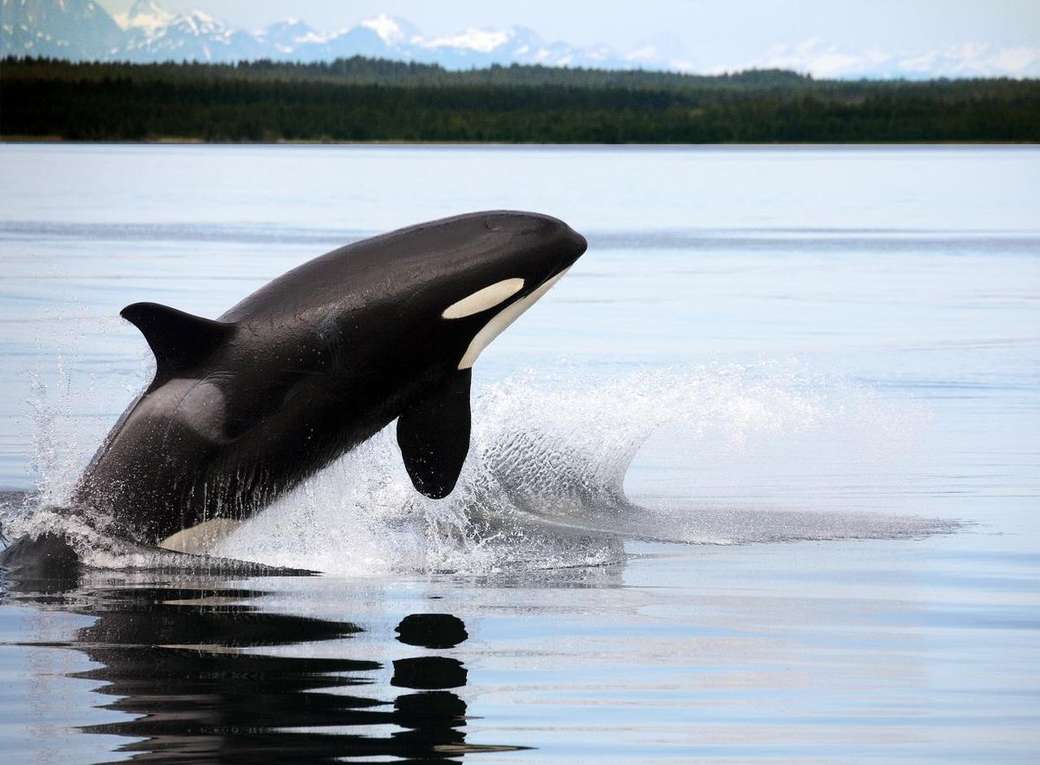
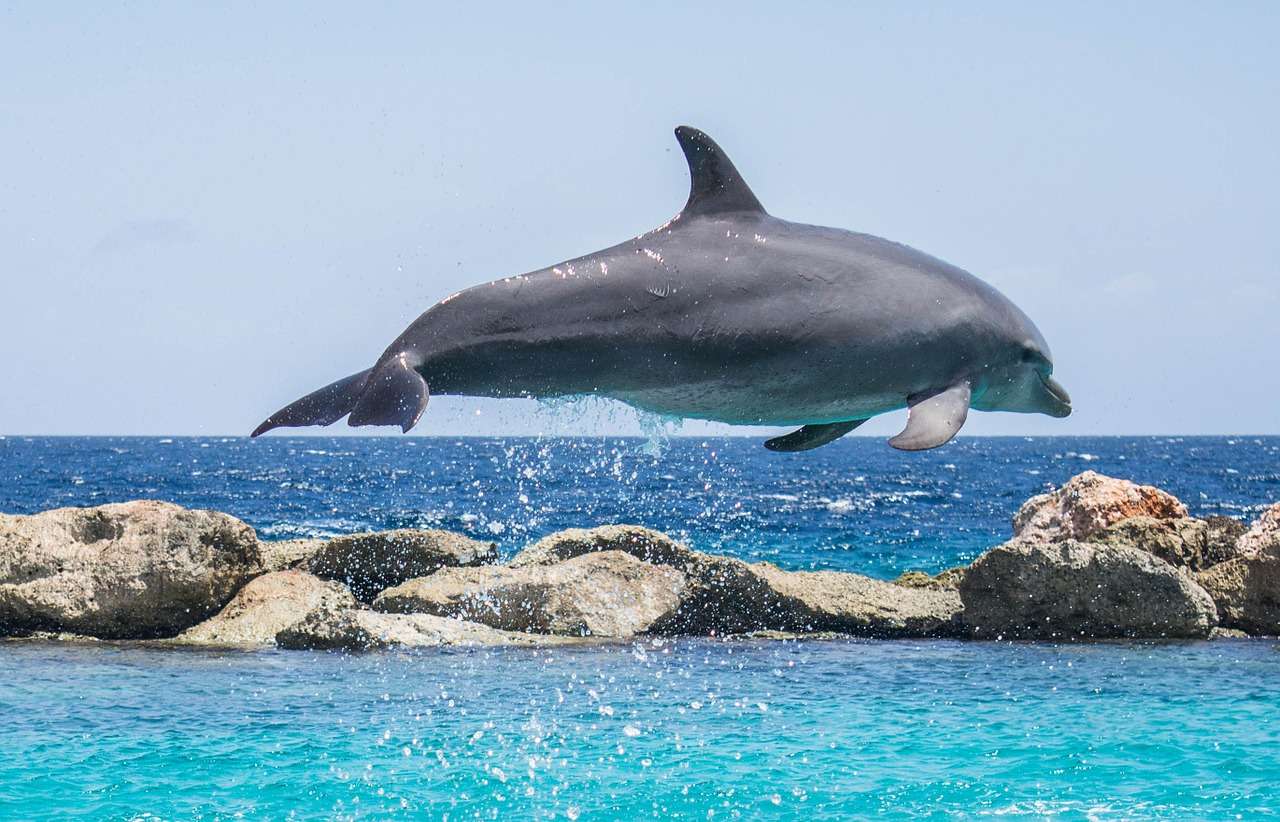
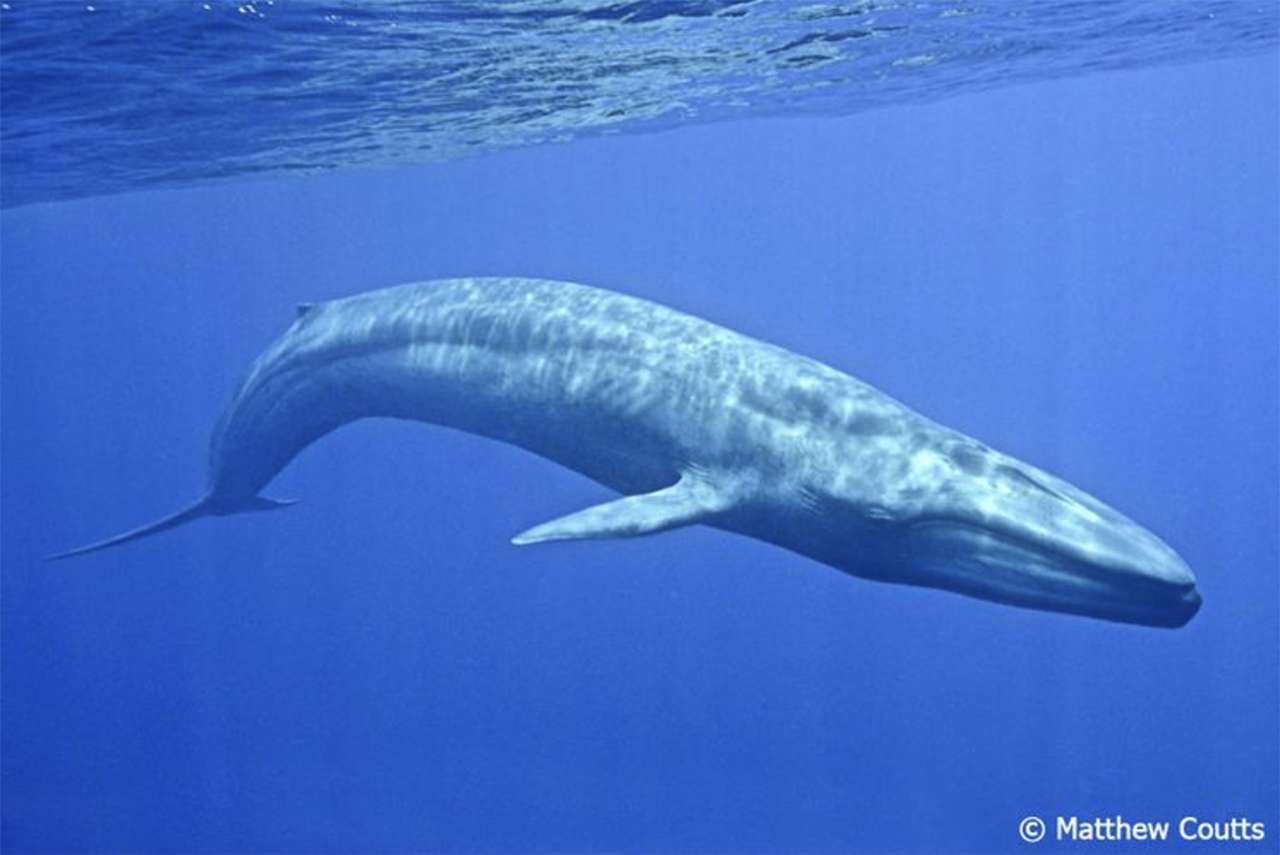
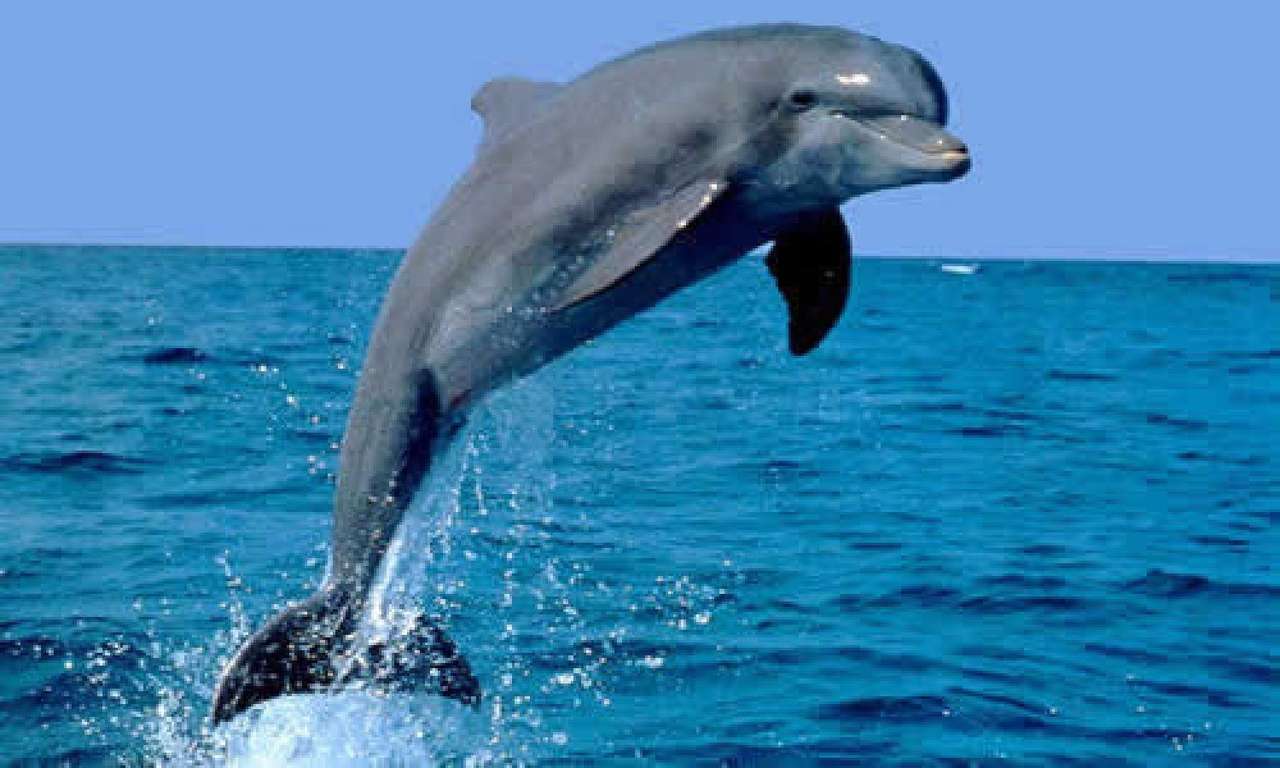




















































Online puzzle Cetacea
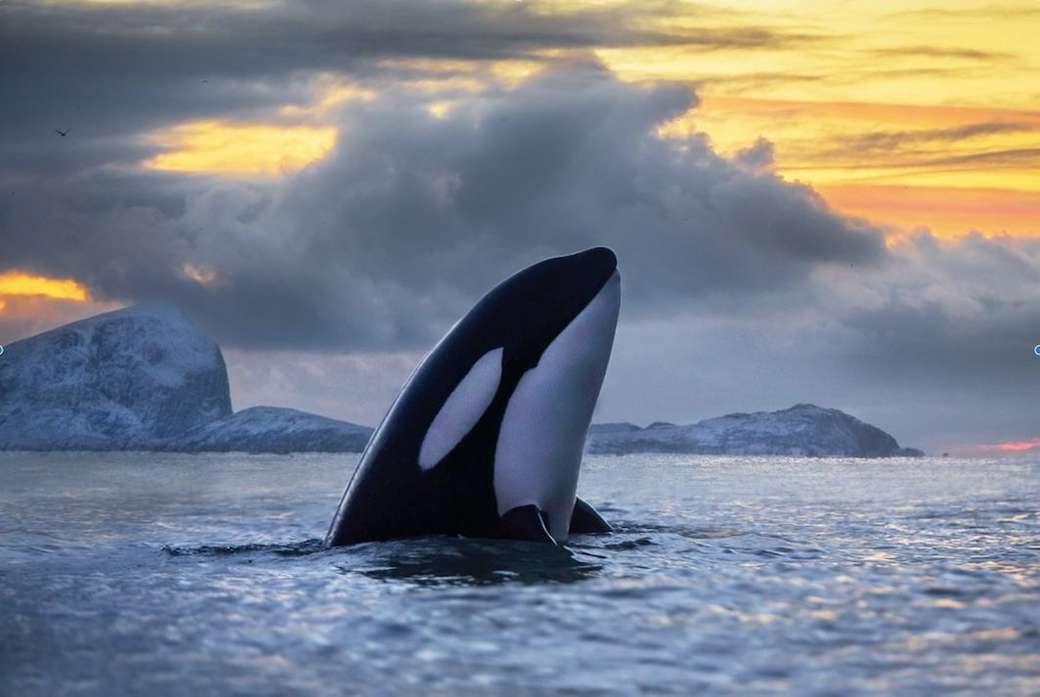
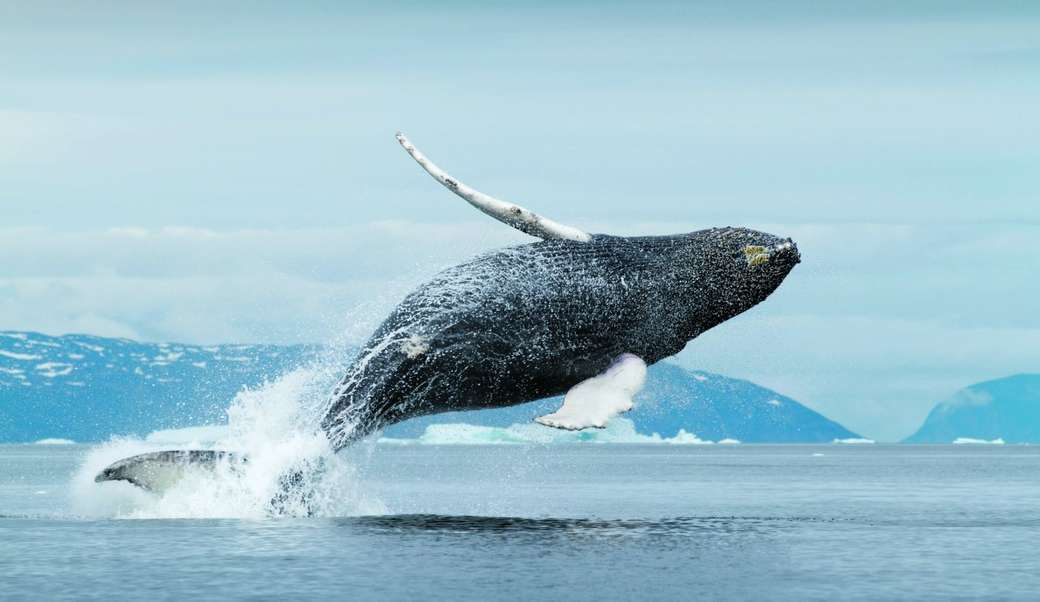
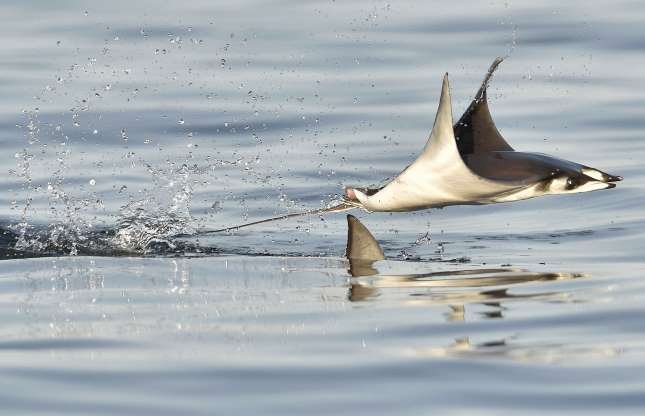
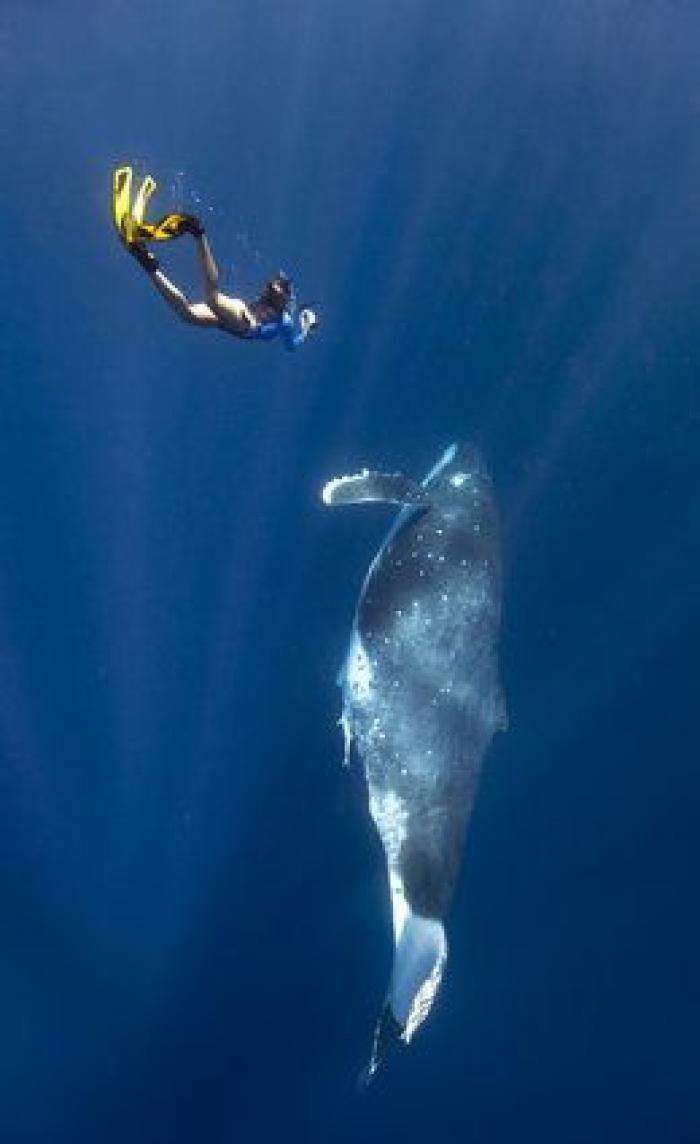
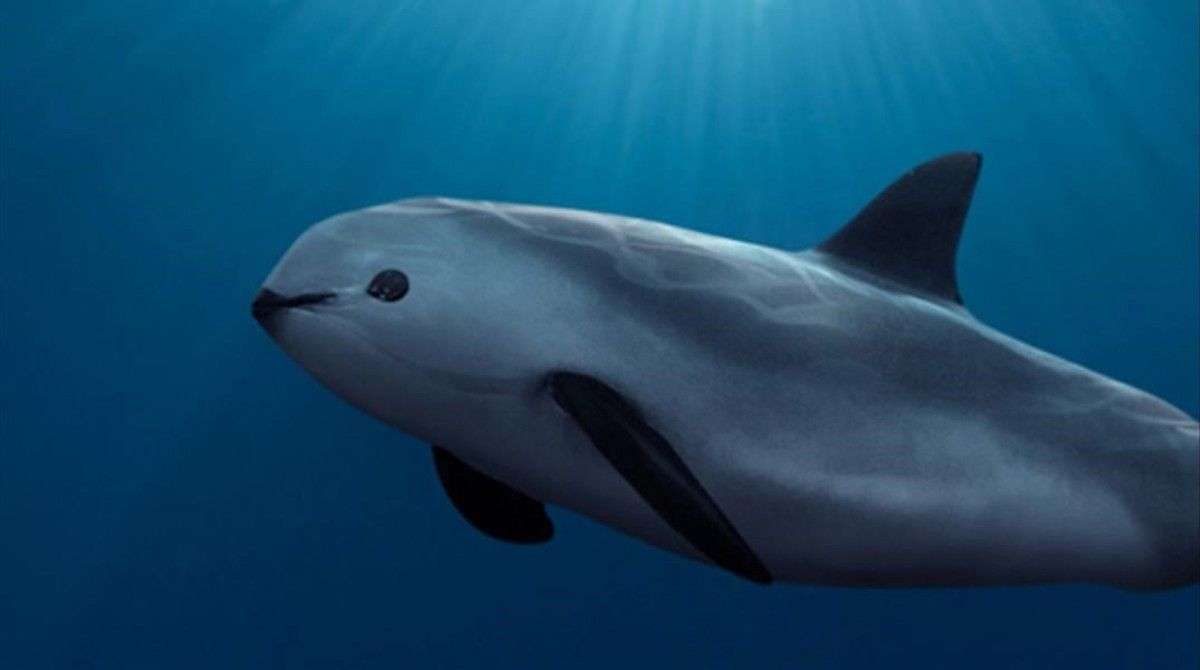
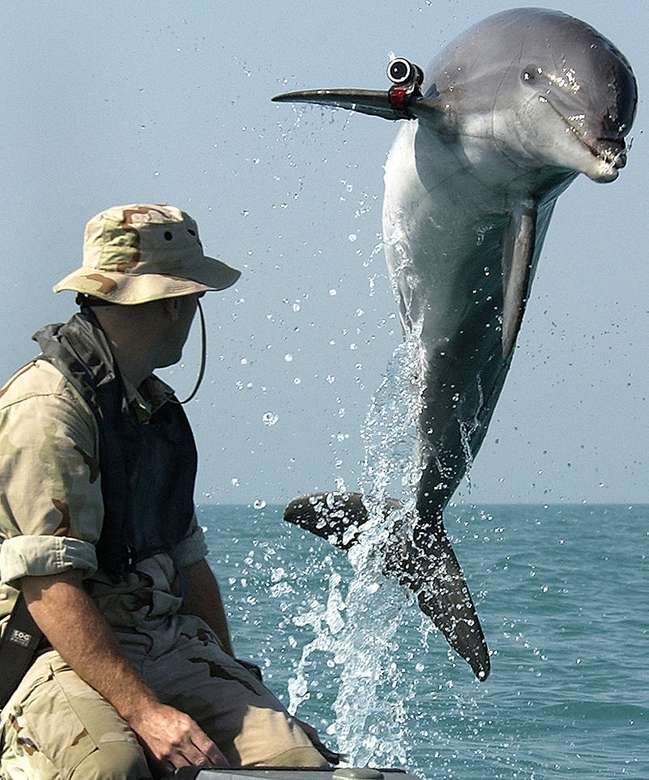
Cetaceans () (from Latin cetus " whale ", from Greek κῆτος kētos "huge fish ") are aquatic mammals constituting the infraorder cetacea. There are around 89 living species, which are divided into two parvorders. The first is the Odontoceti, the toothed whales, which consist of around 70 species, including the dolphin, porpoise, beluga whale, narwhal, sperm whale, and beaked whale. The second is the Mysticeti, the baleen (from Latin balæna, whale ) whales, which have a filter-feeder system, and consist of 15 species divided into 3 families, and include the right whale, bowhead whale, rorqual, pygmy right whale, and gray whale.
The ancient and extinct ancestors of modern whales (Archaeoceti) lived 53 to 45 million years ago. They diverged from even-toed ungulates; their closest living relatives are hippopotamuses and others such as camels and pigs. They were amphibious, and evolved in the shallow waters that separated India from Asia. Around 30 species adapted to a fully oceanic life. Baleen whales split from toothed whales around 34 million years ago.
The smallest cetacean is Maui 's dolphin, at 1 m (3 ft 3 in) and 50 kg (110 lb); the largest is the blue whale, at 29.9 m (98 ft) and 173 t (381,000 lb).