Bioluminescence - online puzzles
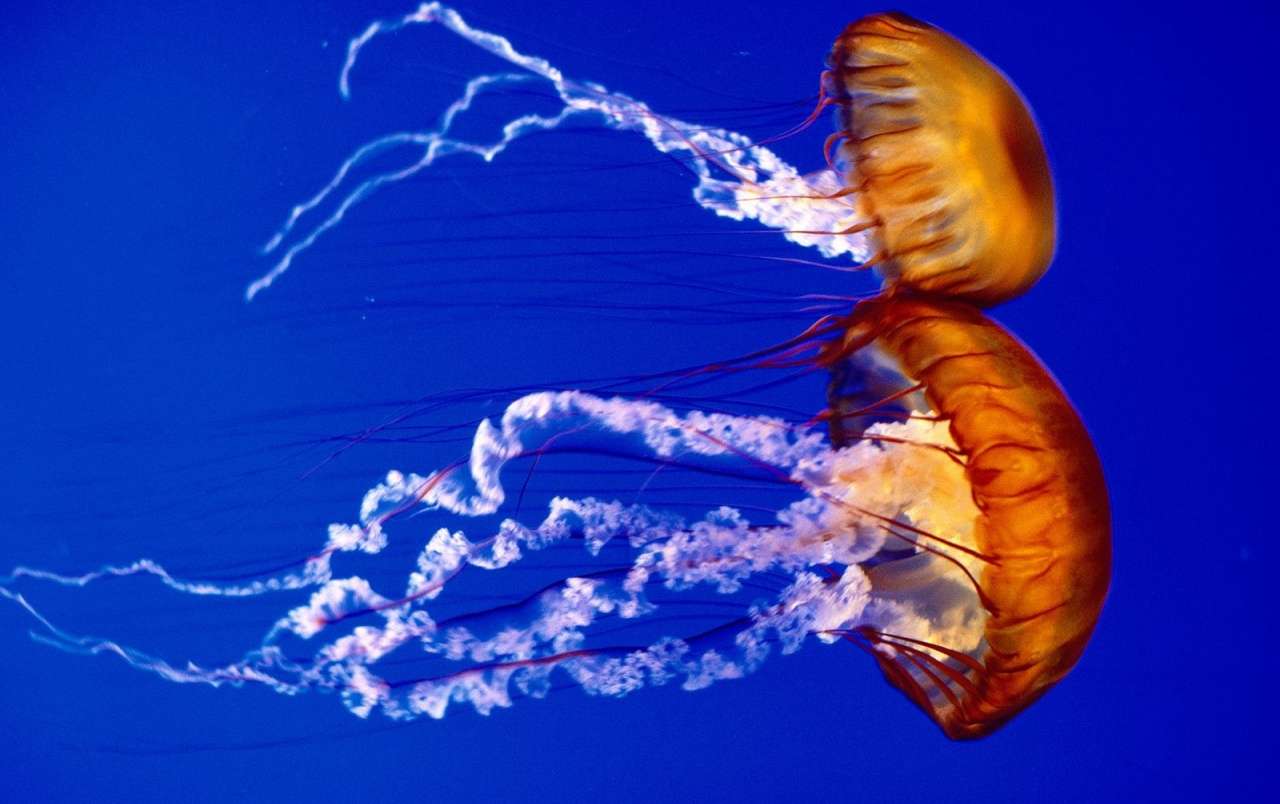
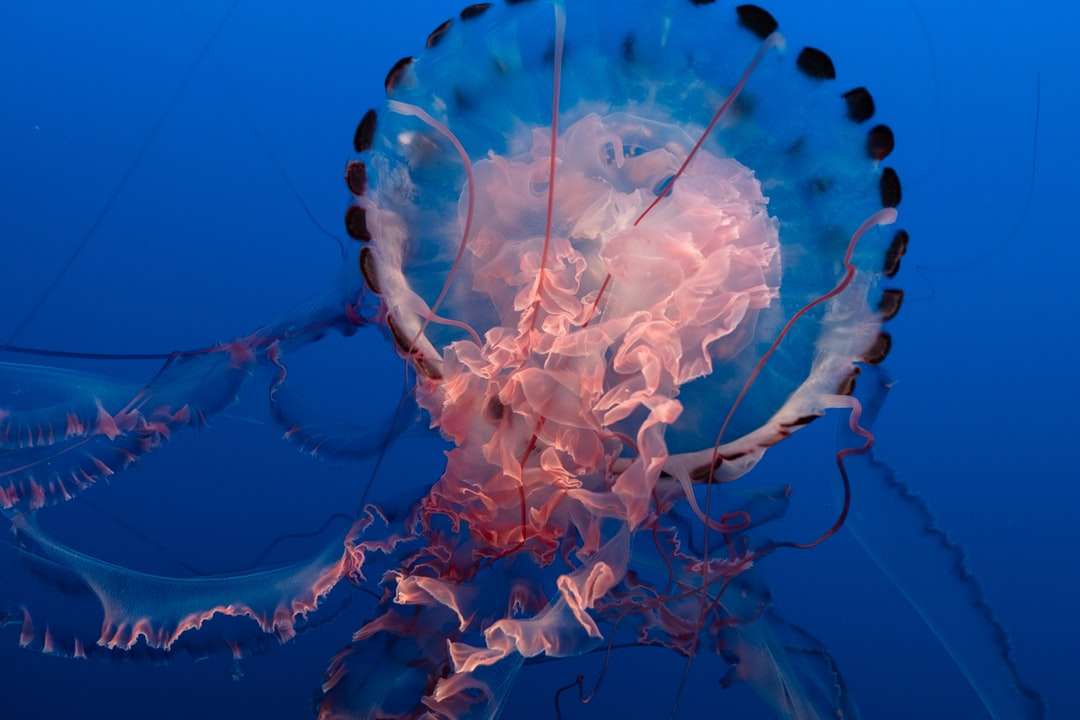
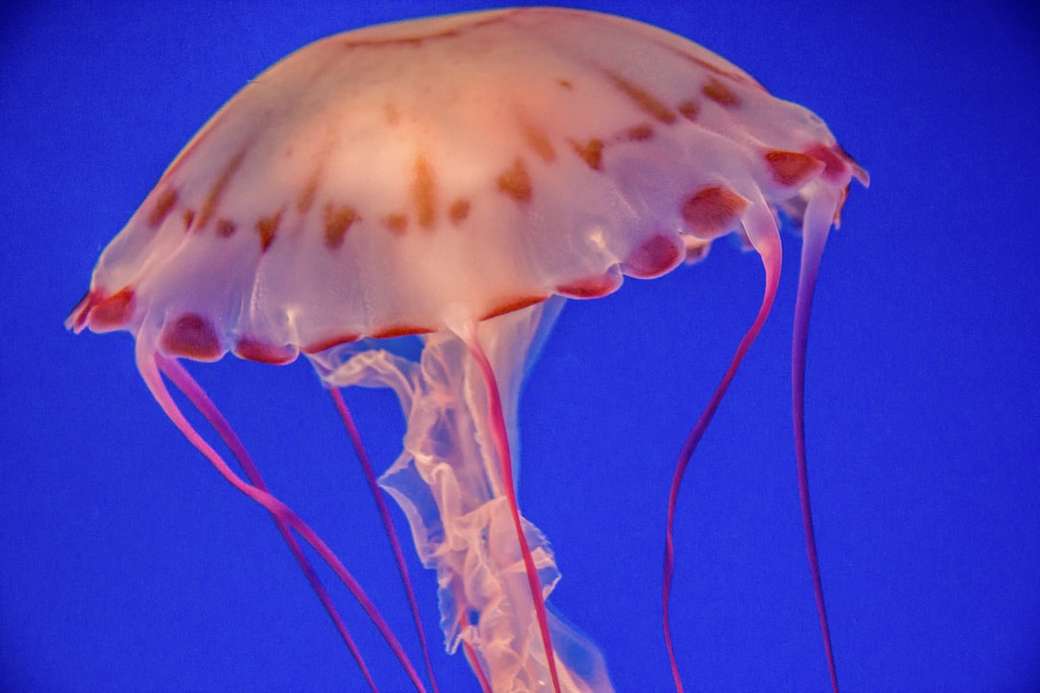
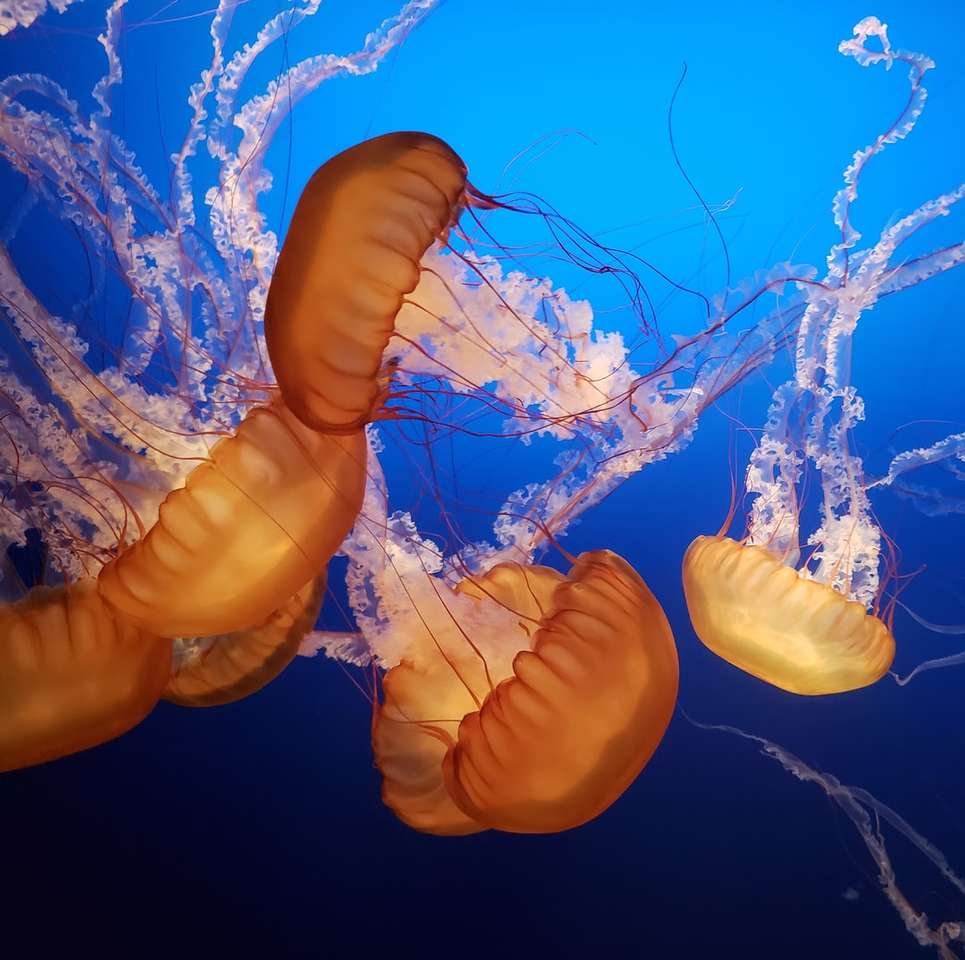
















Online puzzle Bioluminescence
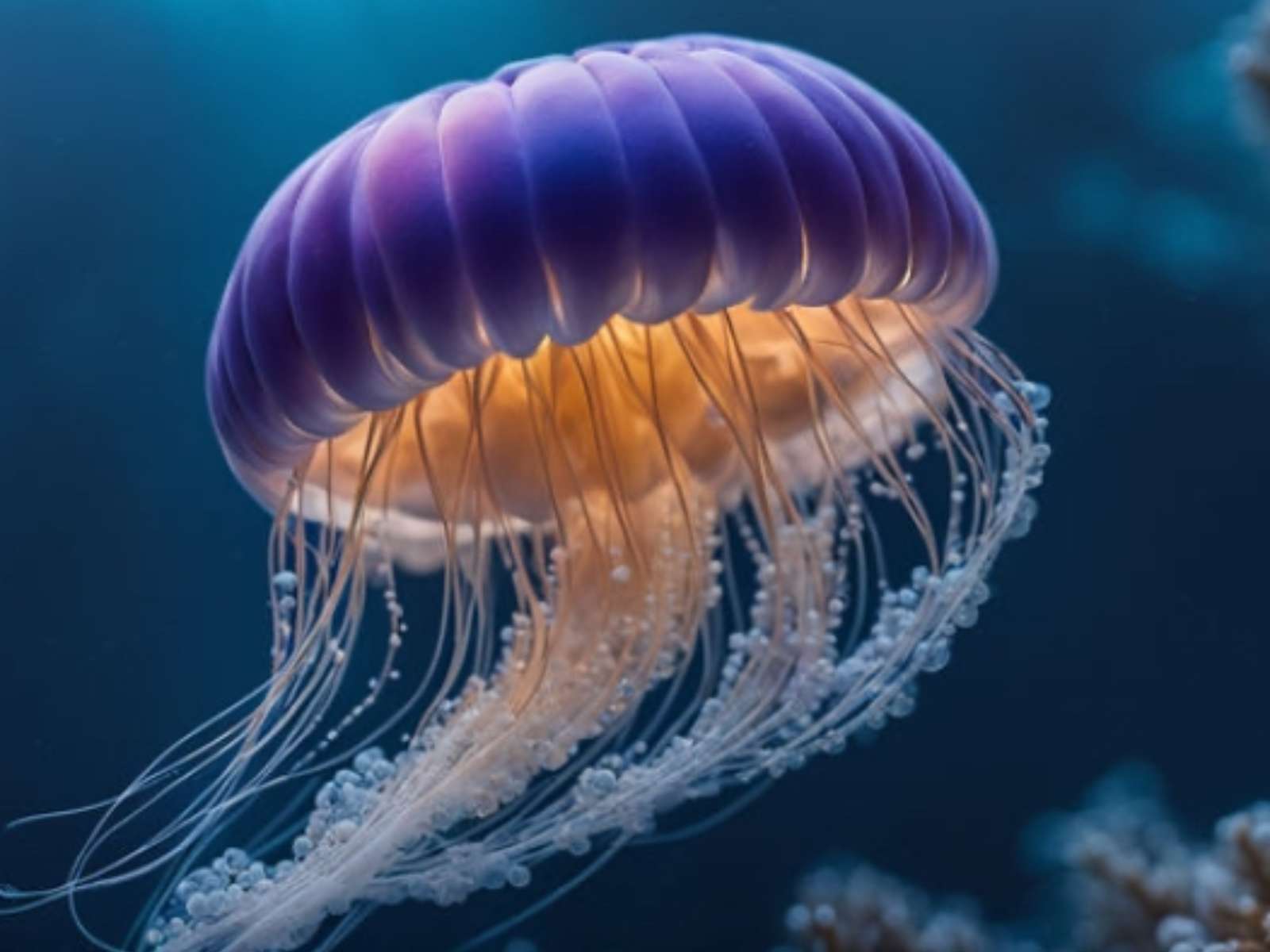
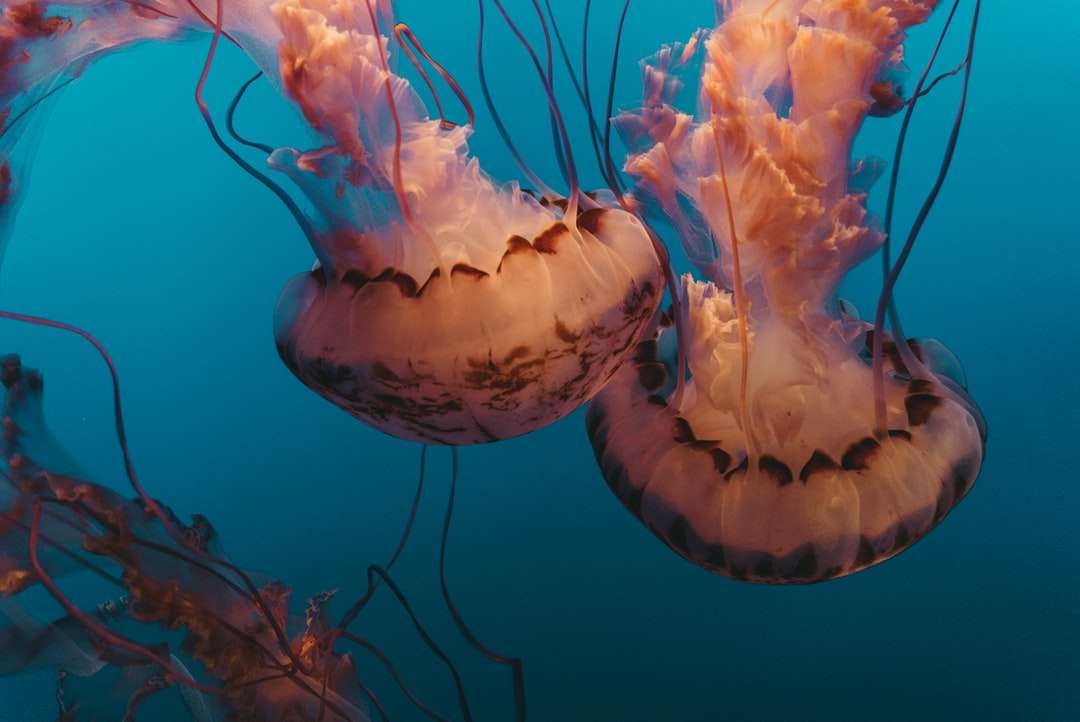
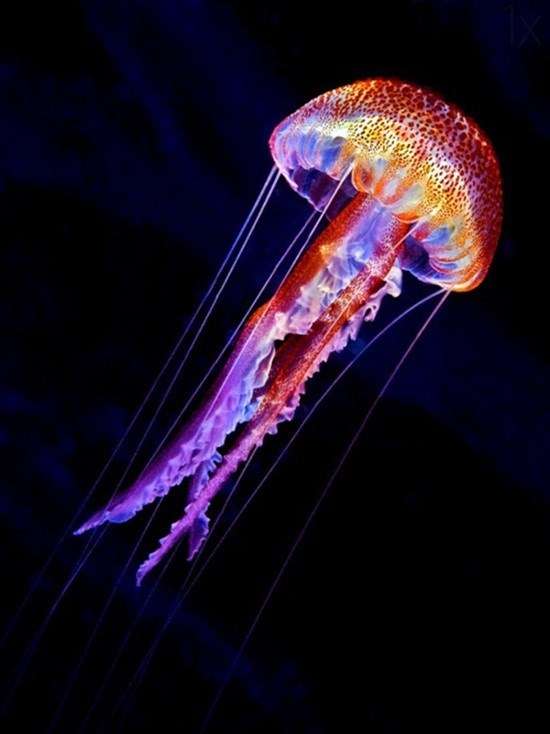
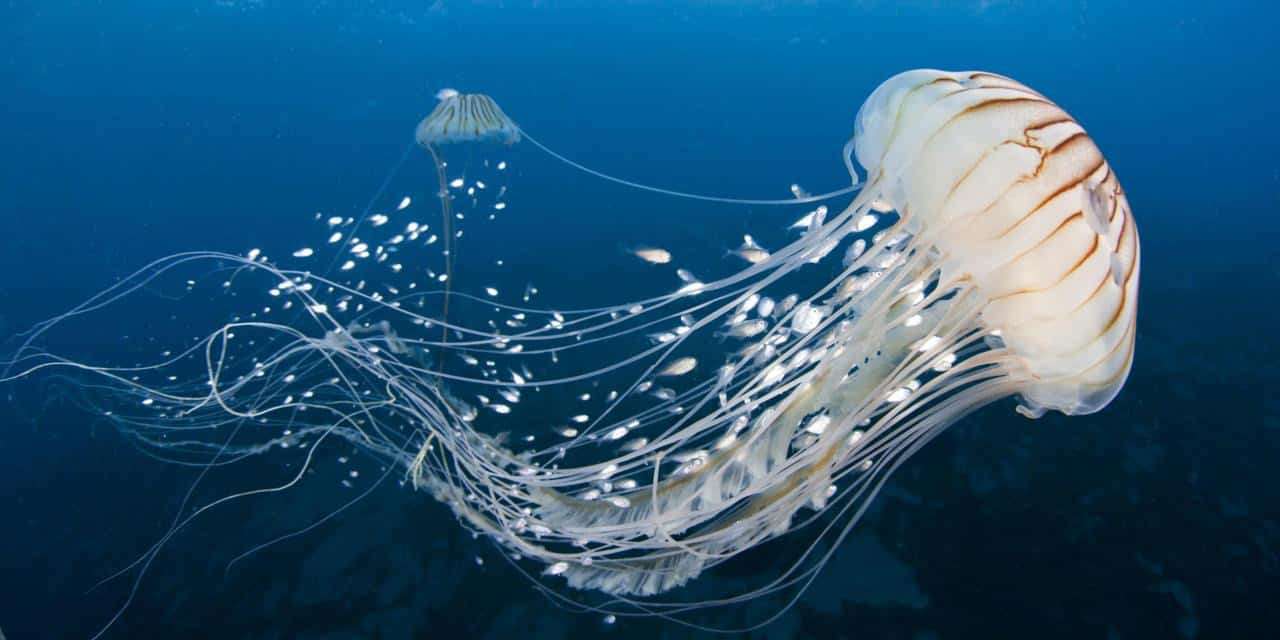
Bioluminescence is the production and emission of light by a living organism. It is a form of chemiluminescence. Bioluminescence occurs widely in marine vertebrates and invertebrates, as well as in some fungi, microorganisms including some bioluminescent bacteria and terrestrial invertebrates such as fireflies. In some animals, the light is bacteriogenic, produced by symbiotic organisms such as Vibrio bacteria; in others, it is autogenic, produced by the animals themselves.
In a general sense, the principal chemical reaction in bioluminescence involves some light -emitting molecule and an enzyme, generally called the luciferin and the luciferase, respectively. Because these are generic names, the luciferins and luciferases are often distinguished by including the species or group, i.e. Firefly luciferin. In all characterized cases, the enzyme catalyzes the oxidation of the luciferin.
In some species, the luciferase requires other cofactors such as calcium or magnesium ions, and sometimes also the energy -carrying molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In evolution, luciferins vary little : one in particular, coelenterazine, is found in eleven different animal (phyla), though in some of these, the animals obtain it through their diet.
