Religions - Church - online puzzles






















































Online puzzle Church (building)
Church (building)
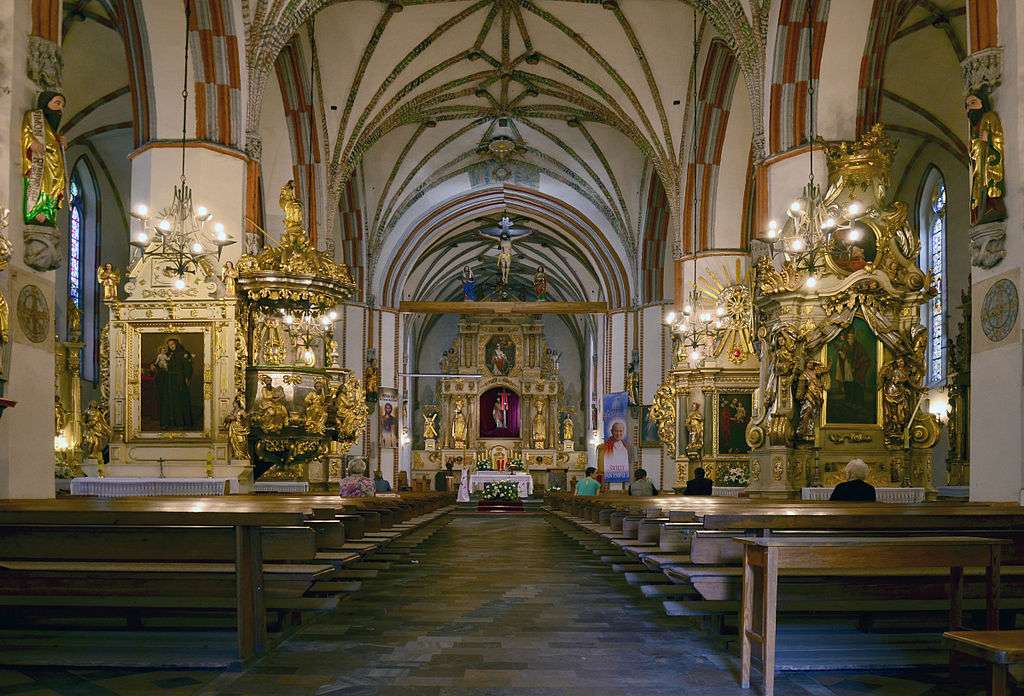
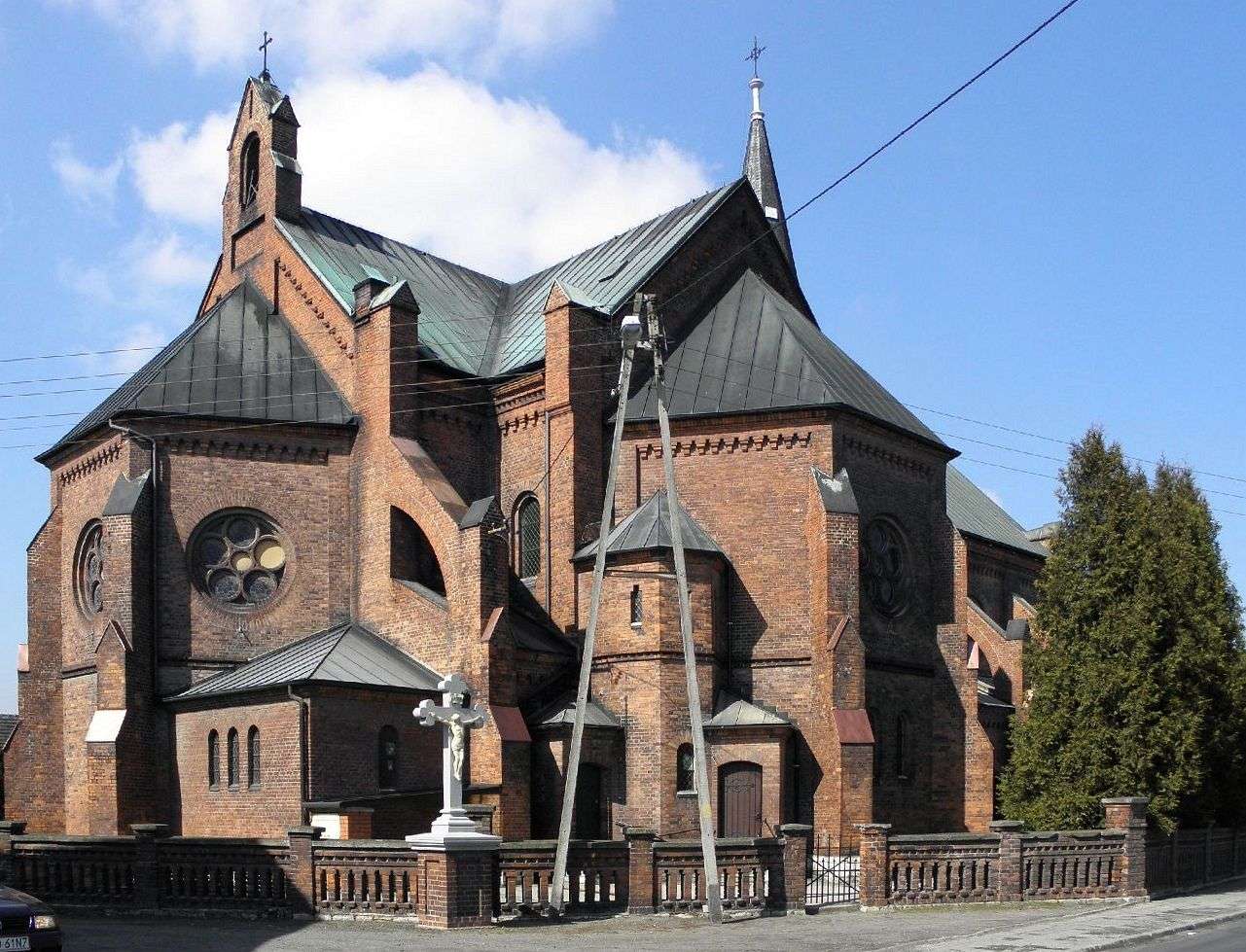
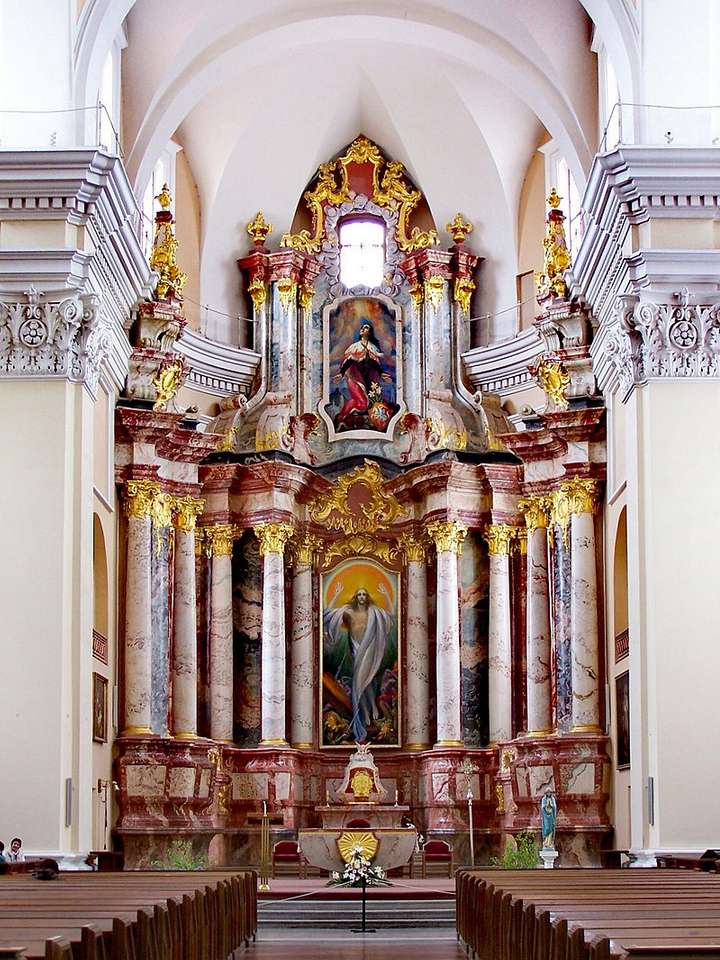
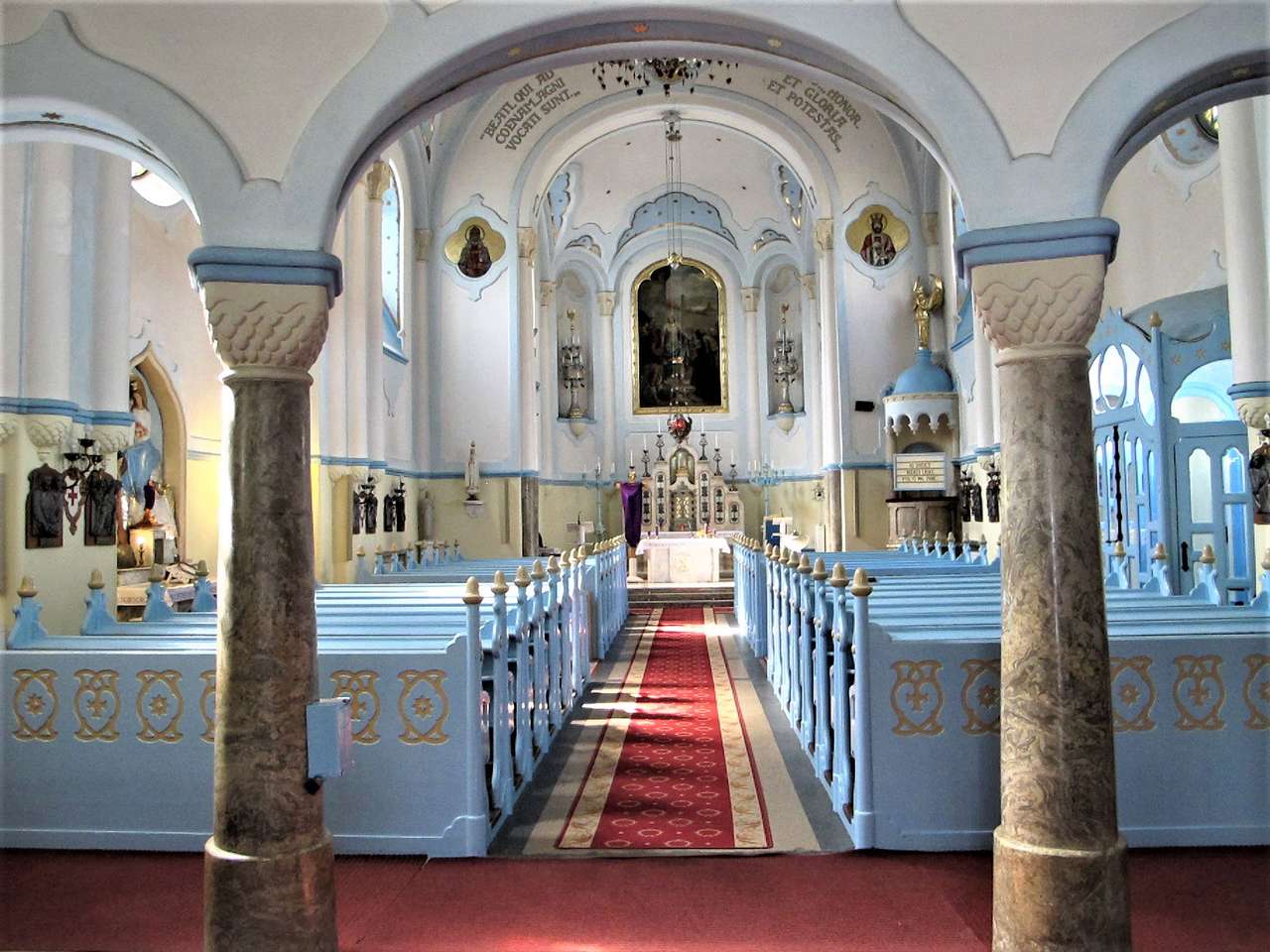
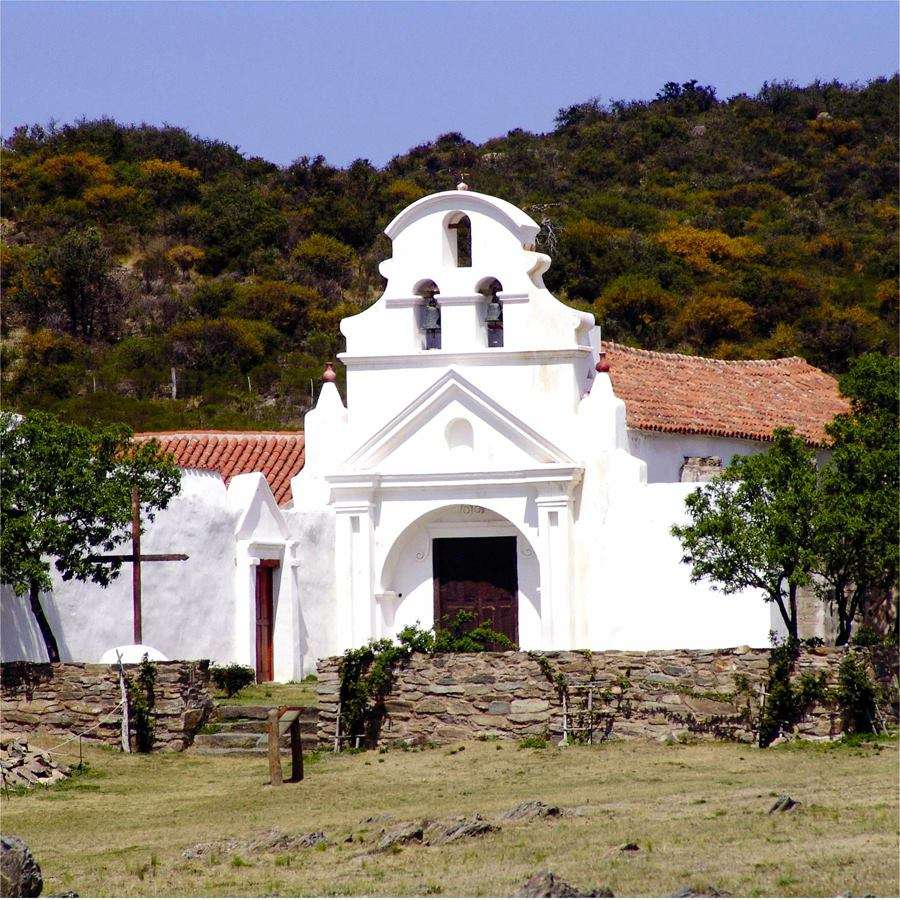
A church, church building, or church house is a building used for Christian worship services and other Christian religious activities. The earliest identified Christian church is a house church founded between 233 and 256.
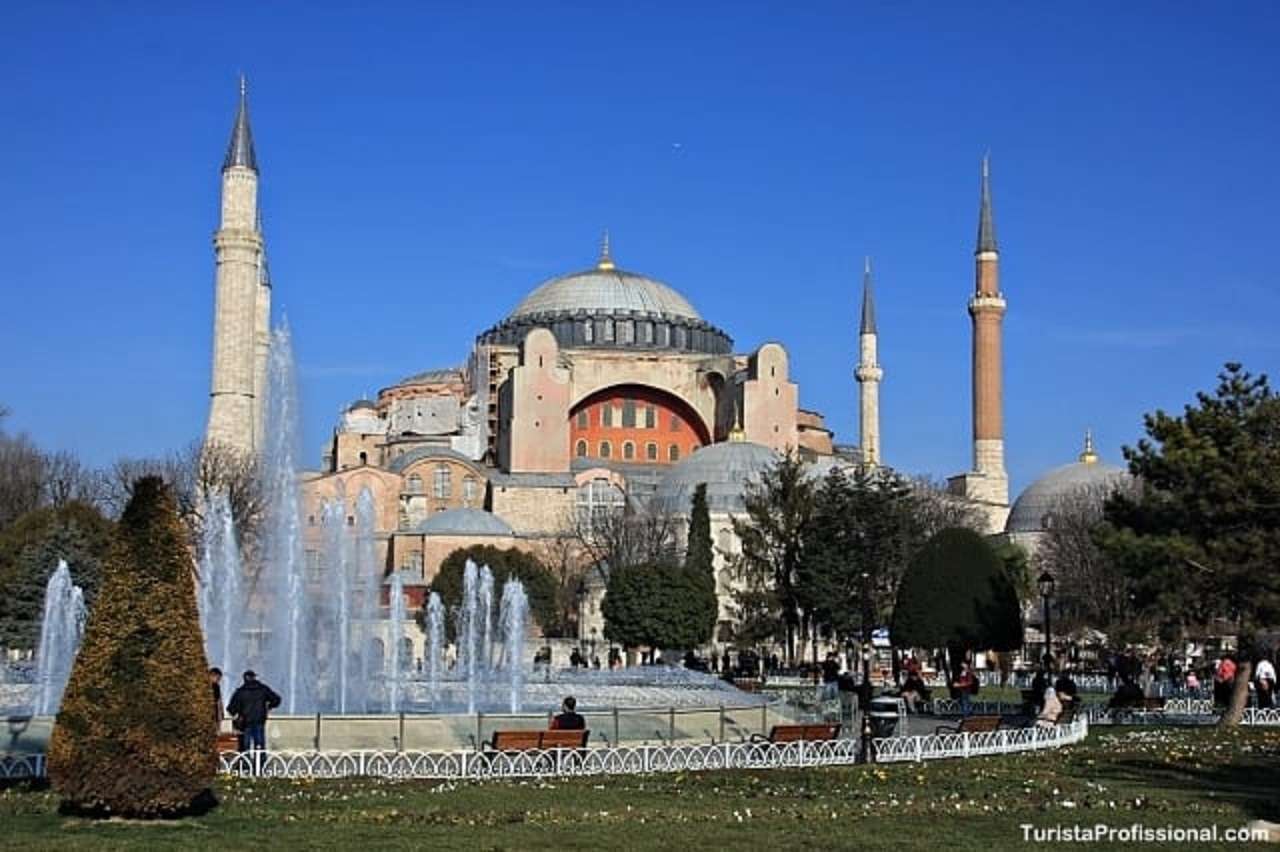
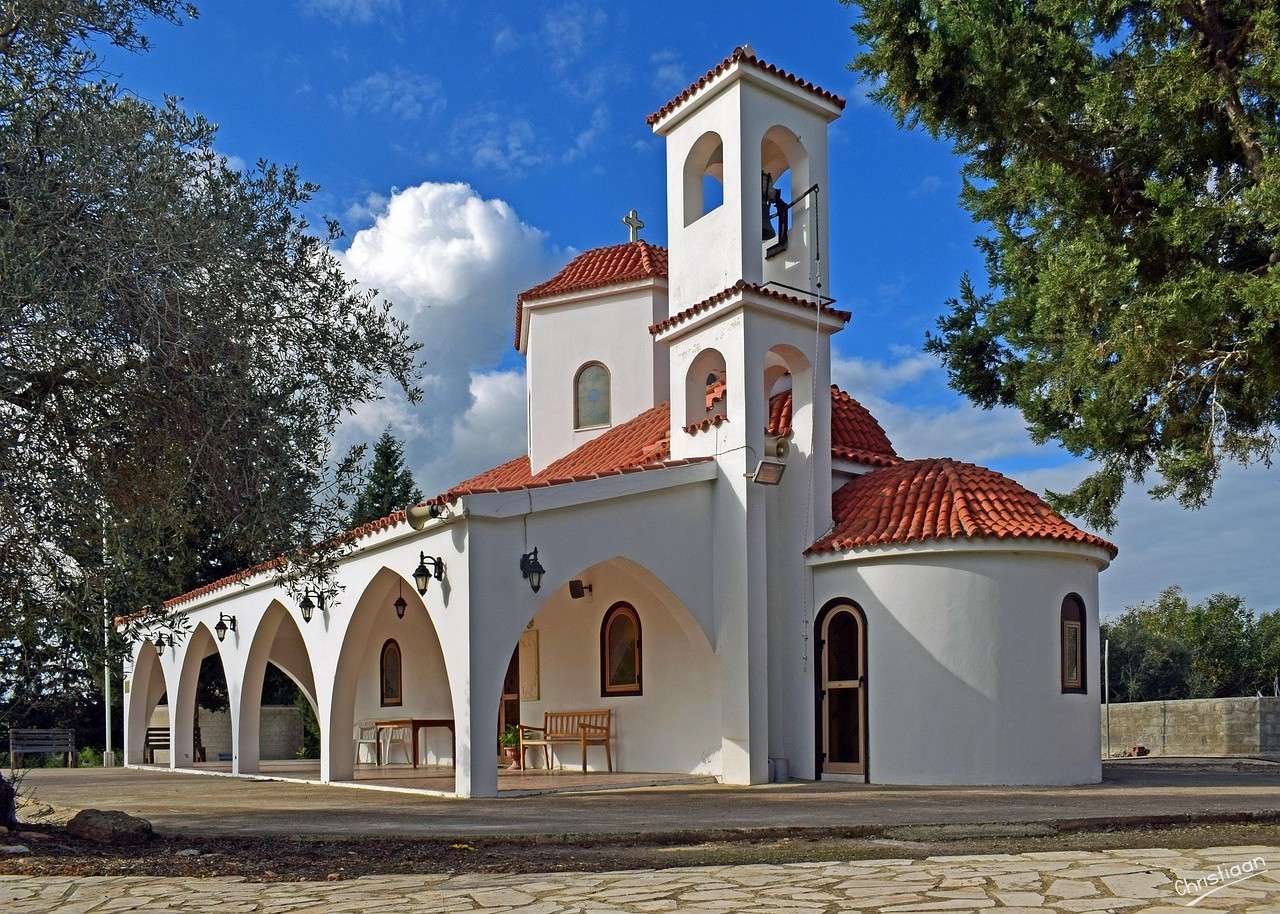
Sometimes, the word church is used by analogy and simplicity for the buildings of other religions, such as mosques and synagogues. Church is also used to describe a body or an assembly of Christian believers, while "the Church" may be used to refer to the worldwide Christian religious community as a whole.In traditional Christian architecture, the plan view of a church often forms a Christian cross with the center aisle and seating representing the vertical beam and the bema and altar forming the horizontal. Towers or domes may inspire contemplation of the heavens. Modern churches have a variety of architectural styles and layouts. Some buildings designed for other purposes have been converted to churches, while many original church buildings have been put to other uses. From the 11th through the 14th centuries, there was a wave of church construction in Western Europe.